Portal:Finland
The Finland Portal


Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, opposite Estonia. Finland has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Helsinki. The majority of the population are ethnic Finns. The official languages are Finnish and Swedish; 84.9 percent of the population speak the first as their mother tongue and 5.1 percent the latter. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to boreal in the north. The land cover is predominantly boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes.
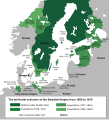
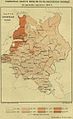
Finland was first settled around 9000 BC after the last Ice Age. During the Stone Age, various cultures emerged, distinguished by different styles of ceramics. The Bronze Age and Iron Ages were marked by contacts with other cultures in Fennoscandia and the Baltic region. From the late 13th century, Finland became part of Sweden as a result of the Northern Crusades. In 1809, as a result of the Finnish War, Finland was captured from Sweden and became an autonomous grand duchy within the Russian Empire. During this period, Finnish art flourished and the independence movement began to take hold. Finland became the first territory in Europe to grant universal suffrage in 1906, and the first in the world to give all adult citizens the right to run for public office. Following the Russian Revolution of 1917, Finland declared its independence. A civil war was fought in Finland the following year, with the Whites emerging victorious. Finland's status as a republic was confirmed in 1919. During World War II, Finland fought against the Soviet Union in the Winter War and the Continuation War, and later against Nazi Germany in the Lapland War. As a result, it lost parts of its territory to the Soviet Union but retained its independence and democracy. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The Symphony No. 8, JS 190, was the final major compositional project of the Finnish composer Jean Sibelius, occupying him intermittently from the mid-1920s until around 1938, though he never published it. During this time Sibelius was at the peak of his fame, a national figure in his native Finland and a composer of international stature. A fair copy of at least the first movement was made, but how much of the Eighth Symphony was completed is unknown. Sibelius repeatedly refused to release it for performance, though he continued to assert that he was working on it even after he had, according to later reports from his family, burned the score and associated material, probably in 1945.
Much of Sibelius's reputation, during his lifetime and subsequently, derived from his work as a symphonist. His Seventh Symphony of 1924 has been widely recognised as a landmark in the development of symphonic form, and at the time there was no reason to suppose that the flow of innovative orchestral works would not continue. However, after the symphonic poem Tapiola, completed in 1926, his output was confined to relatively minor pieces and revisions to earlier works. During the 1930s the Eighth Symphony's premiere was promised to Serge Koussevitzky and the Boston Symphony Orchestra on several occasions, but as each scheduled date approached Sibelius demurred, claiming that the work was not ready for performance. Similar promises made to the British conductor Basil Cameron and to the Finnish Georg Schnéevoigt likewise proved illusory. It is thought that Sibelius's perfectionism and exalted reputation prevented him ever completing the symphony to his satisfaction; he wanted it to be even better than his Seventh. (Full article...)
Selected image -
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that Joe Wirkkunen coached the Finland men's national ice hockey team after receiving a recommendation from Canada?
- ... that Matti Lehtinen, a baritone of the Finnish National Opera and professor of singing at the Sibelius Academy, was the voice of God at age 93?
- ... that the United States severed diplomatic ties with Finland in 1944 because of a personal letter sent to Hitler?
- ... that Finnish-American model Selene Mahri married three millionaires and is credited with inventing the saying "Marriage is a question of give and take. You give. I take"?
- ... that Kimmo Leinonen helped establish both the Finnish Hockey Hall of Fame and the IIHF Hall of Fame?
- ... that the 1972 Finnish film The Sheep Eaters gathered more than a million viewers opposite the 1975 Ice Hockey World Championships match between Finland and the Soviet Union?
WikiProjects

You are invited to participate in Finland WikiProject, a WikiProject dedicated to developing and improving articles about Finland.
More did you know -
- ...that the career of Tiia Piili, four-time FISAF World Champion in sport aerobics, was threatened when she got food poisoning attending a competition in Morocco?
- ...that Erkki Karu founded both Suomi-Filmi and Suomen Filmiteollisuus, the two largest film production companies during the 'Golden Age' of Finnish cinema?
- ...that "Blooddrunk", a track by Finnish band Children of Bodom about self-destructive behaviour, debuted at number one in Finland?
- ...that Taisto Mäki, one of the so-called Flying Finns, was the first man to run 10,000 metres in under half an hour?
- ...that when called by the opposition to quit after the Kauhajoki school shooting, Finnish politician Anne Holmlund refused and compared resigning her post as Interior Minister to "desertion"?

- ... that the asteroid 1536 Pielinen is named after Pielinen Lake (pictured) in Finland?
Nico Erik Rosberg (born 27 June 1985) is a German and Finnish former racing driver and entrepreneur, who competed under the German flag in Formula One from 2006 to 2016. Rosberg won the Formula One World Drivers' Championship in 2016 with Mercedes, and won 23 Grands Prix across 11 seasons.
The only child of Finnish 1982 Formula One World Champion Keke Rosberg and his German wife, he was born in Wiesbaden but was raised primarily in Monaco. Rosberg began competitive kart racing at the age of six and achieved early success, winning regional and national French championships, before moving to European-based series and world championships. At the age of 16, he progressed to car racing, winning nine races to claim the 2002 Formula BMW ADAC Championship with VIVA Racing. He subsequently moved to the higher-tier Formula 3 Euro Series with Team Rosberg in 2003 and 2004 before winning the inaugural GP2 Series championship with ART Grand Prix in 2005. (Full article...)
General images
In the news
- 14 January 2025 – 2024 Baltic Sea submarine cable disruptions, NATO operations
- At the Summit of Baltic Sea Allies in Helsinki, Finland, NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte announces the establishment of the Baltic Sentry military mission, which will strengthen the protection of critical infrastructure in the region, such as energy and communication cables, from "destabilizing acts". (NATO News)
- 3 January 2025 – 2024 Estlink 2 incident
- A district court in Helsinki, Finland, denies a request to release the impounded oil tanker Eagle S, suspected of damaging the Estlink 2 submarine power cable and carrying sanctioned Russian oil. (Al Jazeera)
- 26 December 2024 – 2024 Baltic Sea submarine cable disruptions, Finland–Russia relations
- 2024 Estlink 2 incident
- Finnish border guards and police detain a Russian vessel suspected of damaging the Estlink-2 submarine power cable yesterday. (AP)
- 25 December 2024 – 2024 Estlink 2 incident
- HVDC submarine power cable Estlink 2, which connects the power grids of Estonia and Finland, suffers an unexplained outage with Finnish Prime Minister Petteri Orpo stating that an investigation into the incident is underway. (AP)
- 18 November 2024 – 2024 Baltic Sea submarine cable disruptions
- The C-Lion1 submarine communications cable across the Baltic Sea between Finland and Germany is damaged in what German officials suspect is sabotage. (The Guardian)
Related portals
Northern Europe
Other countries
Selected panorama -
Topics
Categories
Recognized content
Things you can do
- Add the {{Portal|Finland}} template to existing See also sections of Finland-related articles.
- Tag the talk pages of Finland-related articles with the {{WikiProject Finland}} template. (Tip: Use PetScan to find articles not tagged yet by replacing the category "Finnish films" with another category and adjust "Depth" if needed. This tool is helpful for tagging. See also the list of pages not tagged yet.)
- Rate unassessed and unknown-importance articles according to the guidelines. (This tool is helpful for doing these.)
- Translate a Finnish-language article into English.
- Expand a stub into a full article.
- Help with the articles needing attention (watch) and cleanup.
- Create a requested article (watch).
- Support fresh articles (watch).
- Patrol the recent changes.
- Add the following pages to your watchlist:
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus