
ORDER
| Product | Product Code | ORDER | SAFETY DATA | Technical data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2N) 99% Silver Carbonate | AG-CB-02 | Pricing Add to cart only | SDS > | Data Sheet > |
| (3N) 99.9% Silver Carbonate | AG-CB-03 | Pricing Add to cart only | SDS > | Data Sheet > |
| (4N) 99.99% Silver Carbonate | AG-CB-04 | Pricing Add to cart only | SDS > | Data Sheet > |
| (5N) 99.999% Silver Carbonate | AG-CB-05 | Pricing Add to cart only | SDS > | Data Sheet > |
Silver Carbonate Properties (Theoretical)
| Compound Formula | Ag2CO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 275.75 |
| Appearance | Yellow to green powder or chunks |
| Melting Point | 218 °C |
| Boiling Point | N/A |
| Density | 6.077 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in H2O | N/A |
| Exact Mass | 275.794593 |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 273.794922 Da |
| Sensitivity | Light sensitive |
| Storage Temperature | Ambient temperatures |
Silver Carbonate Health & Safety Information
| Signal Word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H318-H410 |
| Hazard Codes | C, N |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305+P351+P338-P310 |
| Risk Codes | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36 |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 2843.29 |
| RTECS Number | FG0700000 |
| Transport Information | UN 3077 9/PG III |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| GHS Pictogram |
Image
Image
|
About Silver Carbonate

 Silver Carbonate is a water insoluble Silver source that can easily be converted to other Silver compounds, such as the oxide by heating (calcination). Carbonate compounds also give off carbon dioxide when treated with dilute acids. Silver Carbonate is generally immediately available in most volumes. High purity, submicron and nanopowder forms may be considered. American Elements produces to many standard grades when applicable, including Mil Spec (military grade); ACS, Reagent and Technical Grade; Food, Agricultural and Pharmaceutical Grade; Optical Grade, USP and EP/BP (European Pharmacopoeia/British Pharmacopoeia) and follows applicable ASTM testing standards. Typical and custom packaging is available. Additional technical, research and safety (MSDS) information is available as is a Reference Calculator for converting relevant units of measurement.
Silver Carbonate is a water insoluble Silver source that can easily be converted to other Silver compounds, such as the oxide by heating (calcination). Carbonate compounds also give off carbon dioxide when treated with dilute acids. Silver Carbonate is generally immediately available in most volumes. High purity, submicron and nanopowder forms may be considered. American Elements produces to many standard grades when applicable, including Mil Spec (military grade); ACS, Reagent and Technical Grade; Food, Agricultural and Pharmaceutical Grade; Optical Grade, USP and EP/BP (European Pharmacopoeia/British Pharmacopoeia) and follows applicable ASTM testing standards. Typical and custom packaging is available. Additional technical, research and safety (MSDS) information is available as is a Reference Calculator for converting relevant units of measurement. Synonyms
Carbonic acid, disilver (1+) salt, Carbonic acid, disilver(1+) salt, Disilver(1+) carbonate, disilver carbonate, silver carbonate on Celite, silver tricarbonate
Chemical Identifiers
| Linear Formula | Ag2CO3 |
|---|---|
| Pubchem CID | 92796 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00003403 |
| EC No. | 208-590-3 |
| IUPAC Name | disilver carbonate |
| Beilstein/Reaxys No. | 6936654 |
| SMILES | [Ag+].[Ag+].[O-]C([O-])=O |
| InchI Identifier | InChI=1S/CH2O3.2Ag/c2-1(3)4;;/h(H2,2,3,4);;/q;2*+1/p-2 |
| InchI Key | KQTXIZHBFFWWFW-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| Standard InchI | |
| Appearance | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Density |
Customers For Silver Carbonate Have Also Viewed
Related Applications, Forms & Industries for Silver Carbonate
Packaging Specifications
Typical bulk packaging includes palletized plastic 5 gallon/25 kg. pails, fiber and steel drums to 1 ton super sacks in full container (FCL) or truck load (T/L) quantities. Research and sample quantities and hygroscopic, oxidizing or other air sensitive materials may be packaged under argon or vacuum. Shipping documentation includes a Certificate of Analysis and Safety Data Sheet (SDS). Solutions are packaged in polypropylene, plastic or glass jars up to palletized 440 gallon liquid totes, and 36,000 lb. tanker trucks.
Related Elements
See more Silver products. Silver (atomic symbol: Ag, atomic number: 47) is a Block D, Group 11, Period 5 element with an atomic weight of 107.8682. 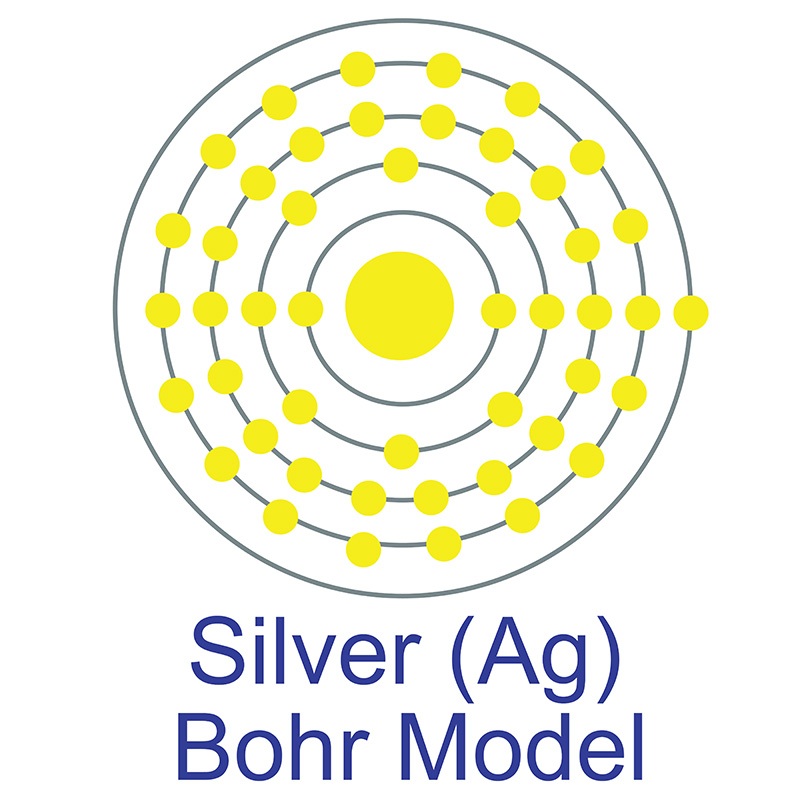 The number of electrons in each of Silver's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s1. The silver atom has a radius of 144 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 203 pm. Silver was first discovered by Early Man prior to 5000 BC. In its elemental form, silver has a brilliant white metallic luster.
The number of electrons in each of Silver's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s1. The silver atom has a radius of 144 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 203 pm. Silver was first discovered by Early Man prior to 5000 BC. In its elemental form, silver has a brilliant white metallic luster.  It is a little harder than gold and is very ductile and malleable, being exceeded only by gold and perhaps palladium. Pure silver has the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all metals and possesses the lowest contact resistance. It is stable in pure air and water, but tarnishes when exposed to ozone, hydrogen sulfide, or air containing sulfur. It is found in copper, copper-nickel, lead, and lead-zinc ores, among others. Silver was named after the Anglo-Saxon word "seolfor" or "siolfur," meaning 'silver'.
It is a little harder than gold and is very ductile and malleable, being exceeded only by gold and perhaps palladium. Pure silver has the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all metals and possesses the lowest contact resistance. It is stable in pure air and water, but tarnishes when exposed to ozone, hydrogen sulfide, or air containing sulfur. It is found in copper, copper-nickel, lead, and lead-zinc ores, among others. Silver was named after the Anglo-Saxon word "seolfor" or "siolfur," meaning 'silver'.
TODAY'S TOP DISCOVERY™!
Los Angeles, CA

