Selanik İmparatorluğu
Görünüm
Selanik İmparatorluğu | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1224-1246 | |||||||||||||
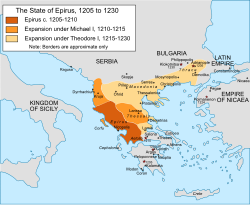
İlk iki hükümdarı Michael I Komnenos Doukas (1205-15) ve Theodore Komnenos Doukas (1215-30) döneminde Epir Prensliği'nin toprak genişlemesinin haritası, Theodore'un "Selanik İmparatorluğu" da dahil. | |||||||||||||
| Tür | İkinci Bulgar İmparatorluğu'nun (1230-37) ve İznik İmparatorluğu'nun (1242-46) vasalı | ||||||||||||
| Başkent | Selanik | ||||||||||||
| Yaygın dil(ler) | Yunanca | ||||||||||||
| Resmî din | Rum Ortodoks Kilisesi | ||||||||||||
| Hükûmet | Monarşi | ||||||||||||
| İmparator, 1242'den sonra Despot | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Tarihî dönem | Orta Çağ | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Selanik İmparatorluğu


Hükümdarlar
[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]Selanik'in Komnenos Dukas hükümdarlarının listesi:
- Theodoros Komnenos Dukas (1224–1230, 1225/27 imparator olarak tac giymiştir)
- Manuil Komnenos Dukas (1230–1237, 1235/37 imparator olarak tac giymiştir)
- İoannis Komnenos Dukas (1237–1242 imparator olarak; 1242–1244 Despot olarak)
- Demetrios Komnenos Dukas (1244–1246 Despot olarak)
- İznik İmparatorluğu tarafından ilhak edilmiştir
Kaynakça
[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]- Özel
- Genel
- Bartusis, Mark C. (1997). The Late Byzantine Army: Arms and Society 1204–1453. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0-8122-1620-2.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest (İngilizce). Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- Finlay, George (1877). A History of Greece: Mediaeval Greece and the empire of Trebizond, A.D. 1204–1461. Clarendon Press.
- Hendy, Michael F. (1999). Catalogue of the Byzantine Coins in the Dumbarton Oaks Collection and in the Whittemore Collection, Volume 4: Alexius I to Michael VIII, 1081–1261 – Part 1: Alexius I to Alexius V (1081–1204). Washington, District of Columbia: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection. ISBN 0-88402-233-1.
- Magdalino, Paul (1989). "Between Romaniae: Thessaly and Epirus in the Later Middle Ages". Arbel, Benjamin; Hamilton, Bernhard; Jacoby, David (Ed.). Latins and Greeks in the Eastern Mediterranean After 1204. Frank Cass & Co. Ltd. ss. 87-110. ISBN 0-71463372-0.
- Nicol, Donald M. (1993). The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453 (İngilizce) (İkinci bas.). Londra: Rupert Hart-Davis Ltd. ISBN 0-246-10559-3.
- Vasilyev, Aleksandr A. (1952). History of the Byzantine Empire, 324–1453. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-80926-3. 30 Ekim 2020 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 23 Haziran 2016.
Konuyla ilgili yayınlar
[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]- Bredenkamp, François (1996). The Byzantine Empire of Thessaloniki (1224–1242). Selanik: Thessaloniki History Center. ISBN 9608433177.
- Stavridou-Zafraka, Alkmini (1999). "The Empire of Thessaloniki (1224–1242). Political Ideology and Reality". Vyzantiaka. Cilt 19. ss. 211-222.