The World Health Organization 2030 goals for Taenia solium: Insights and perspectives from transmission dynamics modelling: CystiTeam Group for Epidemiology and Modelling of Taenia solium Taeniasis/Cysticercosis
- PMID: 31701092
- PMCID: PMC6820453
- DOI: 10.12688/gatesopenres.13068.2
The World Health Organization 2030 goals for Taenia solium: Insights and perspectives from transmission dynamics modelling: CystiTeam Group for Epidemiology and Modelling of Taenia solium Taeniasis/Cysticercosis
Abstract
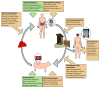
Taenia solium (TS), responsible for porcine cysticercosis, human taeniasis and (neuro)cysticercosis, was included in the World Health Organization neglected tropical disease (NTD) roadmap published in 2012. Targets set in this roadmap have not been met, but T. solium has been included in the consultation process for the new 2030 goals proposed for priority NTDs. Taenia solium transmission dynamics models can contribute to this process. A recent review has compared existing T. solium transmission models, identifying their similarities and differences in structure, parameterization and modelled intervention approaches. While a formal model comparison to investigate the impact of interventions is yet to be conducted, the models agree on the importance of coverage for intervention effectiveness and on the fact that human- and pig-focused interventions can be optimally combined. One of these models, cystiSim, an individual-based, stochastic model has been used to assess field-applicable interventions, some currently under evaluation in on-going trials in Zambia. The EPICYST, population-based, deterministic model has highlighted, based on simulating a generic sub-Saharan Africa setting, the higher efficacy (measured as the percentage of human cysticercosis cases prevented) of biomedical interventions (human and pig treatment and pig vaccination) compared to improved husbandry, sanitation, and meat inspection. Important questions remain regarding which strategies and combinations thereof provide sustainable solutions for severely resource-constrained endemic settings. Defining realistic timeframes to achieve feasible targets, and establishing suitable measures of effectiveness for these targets that can be quantified with current monitoring and evaluation tools, are current major barriers to identifying validated strategies. Taenia solium transmission models can support setting achievable 2030 goals; however, the refinement of these models is first required. Incorporating socio-economic elements, improved understanding of underlying biological processes, and consideration of spatial dynamics are key knowledge gaps that need addressing to support model development.
Keywords: (neuro)cysticercosis; EPICYST; One Health; Taenia solium; cystiSim; mass drug administration; pig vaccination; taeniasis.
Copyright: © 2019 CystiTeam Group for Epidemiology and Modelling of Taenia solium Taeniasis/Cysticercosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modelling for Taenia solium control strategies beyond 2020.Bull World Health Organ. 2020 Mar 1;98(3):198-205. doi: 10.2471/BLT.19.238485. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Bull World Health Organ. 2020. PMID: 32132754 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the impact of intervention strategies against Taenia solium cysticercosis using the EPICYST transmission model.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Feb 9;10(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-1988-9. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28183336 Free PMC article.
-
Taenia solium taeniasis/cysticercosis: From parasite biology and immunology to diagnosis and control.Adv Parasitol. 2021;112:133-217. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2021.03.003. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Adv Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34024358
-
Neurocysticercosis: Current Perspectives on Diagnosis and Management.Front Vet Sci. 2021 May 10;8:615703. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.615703. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34041288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zoonotic Taenia infections with focus on cysticercosis due to Taenia solium in swine and humans.Res Vet Sci. 2021 Jan;134:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.11.015. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Res Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33321377 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding transmission and control of the pork tapeworm with CystiAgent: a spatially explicit agent-based model.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Jul 24;13(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04226-8. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32709250 Free PMC article.
-
The Frequency of Porcine Cysticercosis and Factors Associated with Taenia solium Infection in the Municipality of Tuchín-Córdoba, Colombia.Pathogens. 2024 Apr 11;13(4):311. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13040311. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38668266 Free PMC article.
-
Non-local validated parametrization of an agent-based model of local-scale Taenia solium transmission in North-West Peru.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 27;17(9):e0275247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275247. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36166462 Free PMC article.
-
Managing host-parasite interactions in humans and wildlife in times of global change.Parasitol Res. 2022 Nov;121(11):3063-3071. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07649-7. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 36066742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global variation in force-of-infection trends for human Taenia solium taeniasis/cysticercosis.Elife. 2022 Aug 19;11:e76988. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76988. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35984416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2017 DALYs and HALE Collaborators: Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1859–1922. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32335-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

