A model of anthrax toxin lethal factor bound to protective antigen
- PMID: 16251269
- PMCID: PMC1283467
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508259102
A model of anthrax toxin lethal factor bound to protective antigen
Abstract
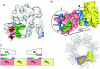
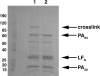
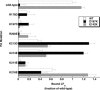
Anthrax toxin is made up of three proteins: the edema factor (EF), lethal factor (LF) enzymes, and the multifunctional protective antigen (PA). Proteolytically activated PA heptamerizes, binds the EF/LF enzymes, and forms a pore that allows for EF/LF passage into host cells. Using directed mutagenesis, we identified three LF-PA contact points defined by a specific disulfide crosslink and two pairs of complementary charge-reversal mutations. These contact points were consistent with the lowest energy LF-PA complex found by using Rosetta protein-protein docking. These results illustrate how biochemical and computational methods can be combined to produce reliable models of large complexes. The model shows that EF and LF bind through a highly electrostatic interface, with their flexible N-terminal region positioned at the entrance of the heptameric PA pore and thus poised to initiate translocation in an N- to C-terminal direction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural determinants for the binding of anthrax lethal factor to oligomeric protective antigen.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 20;281(3):1630-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511164200. Epub 2005 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16293620
-
Interactions of anthrax lethal factor with protective antigen defined by site-directed spin labeling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):1868-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018965108. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21262847 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking anthrax lethal toxin at the protective antigen channel by using structure-inspired drug design.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 18;102(42):15075-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507488102. Epub 2005 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16214885 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane translocation by anthrax toxin.Mol Aspects Med. 2009 Dec;30(6):413-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jun 27. Mol Aspects Med. 2009. PMID: 19563824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthrax toxin: receptor binding, internalization, pore formation, and translocation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:243-65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142728. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17335404 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional insights into the first Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein of the Vpb4 fold, active against western corn rootworm.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 20;16(12):e0260532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260532. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34928980 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of Non-Living Anthrax Vaccine Candidates in Cattle and Protective Efficacy of Immune Sera in A/J Mouse Model Compared to the Sterne Live Spore Vaccine.Pathogens. 2020 Jul 10;9(7):557. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9070557. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32664259 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic structures of anthrax toxin protective antigen channels bound to partially unfolded lethal and edema factors.Nat Commun. 2020 Feb 11;11(1):840. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14658-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32047164 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate and selective quantification of anthrax protective antigen in plasma by immunocapture and isotope dilution mass spectrometry.Analyst. 2019 Mar 25;144(7):2264-2274. doi: 10.1039/c8an02479k. Analyst. 2019. PMID: 30810119 Free PMC article.
-
A bivalent protein r-PB, comprising PA and BclA immunodominant regions for comprehensive protection against Bacillus anthracis.Sci Rep. 2018 May 8;8(1):7242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25502-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29740033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collier, R. J. & Young, J. A. (2003) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19, 45-70. - PubMed
-
- Duesbery, N. S., Webb, C. P., Leppla, S. H., Gordon, V. M., Klimpel, K. R., Copeland, T. D., Ahn, N. G., Oskarsson, M. K., Fukasawa, K., Paull, K. D. & Vande Woude, G. F. (1998) Science 280, 734-737. - PubMed
-
- Vitale, G., Pellizzari, R., Recchi, C., Napolitani, G., Mock, M. & Montecucco, C. (1998) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 248, 706-711. - PubMed
-
- Molloy, S. S., Bresnahan, P. A., Leppla, S. H., Klimpel, K. R. & Thomas, G. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 16396-16402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

