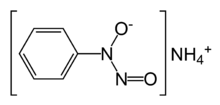
Cupferron
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
cupferron
ammonium N-nitrosophenylhydroxylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.713 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H9N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 155.157 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 150 to 155 °C (302 to 311 °F; 423 to 428 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H315, H319, H335, H351 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cupferron is jargon for the ammonium salt of the conjugate base derived from N-nitroso-N-phenylhydroxylamine. This conjugate base is abbreviated as CU−. It once was a common reagent for the complexation of metal ions, being of interest in the area of qualitative inorganic analysis. Its formula is NH4[C6H5N(O)NO]. The anion binds to metal cations through the two oxygen atoms, forming five-membered chelate rings.
Synthesis and complexes
[edit]
Cupferron is prepared from phenylhydroxylamine and an NO+ source:[1]
- C6H5NHOH + C4H9ONO + NH3 → NH4[C6H5N(O)NO] + C4H9OH
Being a bidentate mono-anionic ligand, CU− forms complexes analogous to those produced with acetylacetonate. Illustrative complexes include Cu(CU)2, Fe(CU)3, and Zr(CU)4.[2][3][4]
References
[edit]- ^ C. S. Marvel (1925). "Cupferron". Organic Syntheses. 4: 19. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.004.0019.
- ^ Elerman, Y.; Atakol, O.; Svoboda, I.; Geselle, M. (1995). "Bis(cupferronato)copper(II), [Cu(C6H5N2O2)2]". Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 51 (8): 1520–1522. doi:10.1107/S0108270195002770.
- ^ Van Der Helm, D.; Merritt, L. L.; Degeilh, R.; MacGillavry, C. H. (1965). "The Crystal Structure of IIron Cupferron Fe(O2N2C6H5)3". Acta Crystallographica. 18 (3): 355–362. doi:10.1107/S0365110X65000816.
- ^ Mark, Wanda; Aava, Ulf; Haaland, A.; Resser, Dag; Rasmussen, S. E.; Sunde, Erling; Sørensen, Nils Andreas (1970). "The Crystal Structure of Zirconium Cupferrate, Zr(C6H5N2O2)4". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 24: 1398–1414. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-1398.
