Retinal: Difference between revisions
Hairy Dude (talk | contribs) →Vitamin A metabolism: {{block indent}} Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
|||
| (340 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Vitamin A aldehyde, a polyene chromophore}} |
|||
{{chembox |
|||
{{Distinguish|Retinol}} |
|||
| ImageFile = Retinal structure.png |
|||
{{About|the molecule|the anatomical feature|Retina}} |
|||
| ImageSize = |
|||
{{Chembox |
|||
| IUPACName = |
|||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| OtherNames = |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 444085949 |
|||
| Formula = C<sub>20</sub>H<sub>28</sub>O |
|||
| Name = All-trans-retinal |
|||
| PubChem = 1070 |
|||
| ImageFile = All-trans-Retinal.svg |
|||
| SMILES = |
|||
| ImageSize = 250 |
|||
| MolarMass= 284.436 |
|||
| ImageAlt = Skeletal formula of retinal |
|||
| Appearance = |
|||
| ImageFile1 = Retinal 3D ball.png |
|||
| ImageSize1 = 260 |
|||
| ImageAlt1 = Ball-and-stick model of the retinal molecule |
|||
| IUPACName = Retinal |
|||
| SystematicName = (2''E'',4''E'',6''E'',8''E'')-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal |
|||
| OtherNames = {{Bulleted list|Retinene|Retinaldehyde|Vitamin A aldehyde|RAL}} |
|||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
|||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} |
|||
| CASNo = 116-31-4 |
| CASNo = 116-31-4 |
||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| Density= |
|||
| UNII = RR725D715M |
|||
| MeltingPt= 63 °C |
|||
| PubChem = 638015 |
|||
| BoilingPt= |
|||
| |
| = |
||
| ChEBI = 17898 |
|||
| StdInChI = 1S/C20H28O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,15H,7,10,14H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ |
|||
| StdInChIKey = NCYCYZXNIZJOKI-OVSJKPMPSA-N |
|||
| SMILES = CC1=C(C(CCC1)(C)C)/C=C/C(=C/C=C/C(=C/C=O)/C)/C}} |
|||
|Section2={{Chembox Properties |
|||
| C=20 | H=28 | O=1 |
|||
| Appearance = Orange crystals from [[petroleum ether]]<ref name="Merck">''Merck Index'', 13th Edition, '''8249'''</ref> |
|||
| Density = |
|||
| MeltingPtC = 61 to 64 |
|||
| MeltingPt_ref = <ref name="Merck"/> |
|||
| BoilingPt = |
|||
| Solubility = Nearly insoluble |
|||
| SolubleOther = Soluble |
|||
| Solvent = fat}} |
|||
|Section7={{Chembox Hazards |
|||
| MainHazards = |
| MainHazards = |
||
| FlashPt = |
| FlashPt = |
||
| |
| = |
||
|Section8={{Chembox Related |
|||
| OtherFunction = |
|||
| OtherFunction_label = |
|||
| OtherCompounds = [[retinol]]; [[retinoic acid]]; [[beta-carotene]]; [[dehydroretinal]]; 3-hydroxyretinal; 4-hydroxyretinal}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Retinal''', technically called '''retinene<sub>1</sub>''' or '''retinaldehyde''', is a light-sensitive [[retinene]] molecule found in the [[photoreceptor cell]]s of the [[retina]]. Retinal is the fundamental [[chromophore]] involved in the transduction of [[light]] into visual signals, i.e. nerve impulses, in the [[visual system]] of the [[central nervous system]]. |
|||
'''Retinal''' (also known as '''retinaldehyde''') is a [[polyene]] [[chromophore]]. Retinal, bound to proteins called [[opsin]]s, is the chemical basis of [[visual phototransduction]], the light-detection stage of [[visual perception]] (vision). |
|||
==Overview== |
|||
The molecule that takes part in the initial step in the [[visual cycle|vision process]], [[rhodopsin]], has two components called 11-cis retinal and [[opsin]]. Retinal is a light-sensitive derivative of [[vitamin A]], and opsin is a protein molecule. Rhodopsin is found in the [[rod cell]]s of the eye. 11-cis retinal is a powerful absorber of light because it is a [[polyene]]; its 6 alternating single and double bonds make up a long conjugated electron network. When no light is present, the 11-cis retinal molecule is found in a "bent (cis) configuration" (''fig A''), and as such it is attached to the opsin molecule in a stable arrangement: |
|||
Some microorganisms use retinal to convert light into metabolic energy. One study suggests that approximately three billion years ago, most living organisms on Earth used retinal, rather than [[chlorophyll]], to convert sunlight into energy. Because retinal absorbs mostly green light and transmits purple light, this gave rise to the [[Purple Earth hypothesis]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=DasSarma |first1=Shiladitya |last2=Schwieterman |first2=Edward W. |date=2018 |title=Early evolution of purple retinal pigments on Earth and implications for exoplanet biosignatures |journal=International Journal of Astrobiology |language=en |publication-date=2018-10-11 |volume=20 |issue=3 |pages=241–250 |doi=10.1017/S1473550418000423 |s2cid=119341330 |issn=1473-5504|doi-access=free |arxiv=1810.05150 }}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:RetinalCisandTrans.png|375px|left|thumb|'''Retinal molecule''' - straightens in response to a [[photon]] γ (light), of the correct wavelength]] |
|||
Retinal itself is considered to be a form of [[vitamin A]] when eaten by an animal. There are many forms of vitamin A, all of which are converted to retinal, which cannot be made without them. The number of different molecules that can be converted to retinal varies from species to species. Retinal was originally called '''[[retinene]]''',<ref name=Wald1934>{{cite journal |last1=Wald |first1=George |title=Carotenoids and the Vitamin A Cycle in Vision |journal=Nature |date=14 July 1934 |volume=134 |issue=3376 |pages=65 |doi=10.1038/134065a0 |bibcode=1934Natur.134...65W |s2cid=4022911|doi-access=free }}</ref> and was renamed<ref name=Wald1968>{{cite journal |last1=Wald |first1=G. |title=Molecular basis of visual excitation |journal=Science |date=11 October 1968 |volume=162 |issue=3850 |pages=230–9 |pmid=4877437 |doi=10.1126/science.162.3850.230 |bibcode=1968Sci...162..230W}}</ref> after it was discovered to be '''vitamin A [[aldehyde]]'''.<ref name=Morton1944>{{cite journal |last1=MORTON |first1=R. A. |last2=GOODWIN |first2=T. W. |title=Preparation of Retinene in Vitro |journal=Nature |date=1 April 1944 |volume=153 |issue=3883 |pages=405–406 |doi=10.1038/153405a0 |bibcode=1944Natur.153..405M |s2cid=4111460}}</ref><ref name=Ball1946>{{cite journal |last1=Ball |first1=S. |last2=Goodwin |first2=T. W. |last3=Morton |first3=R. A. |title=Retinene1-vitamin A aldehyde. |journal=The Biochemical Journal |date=1946 |volume=40 |issue=5–6 |pages=lix |pmid=20341217}}</ref> |
|||
When light strikes the retina, a retinal molecule may absorb a [[photon]], promoting it into an excited electronic state. The nature of the excited state is not well understood, but it is known that within 200 [[femtosecond]]s it returns to the ground electronic state.<ref name='Van Dorst'>{{cite journal | title = Quantumchemische berekeningen aan retinal-modelstoffen | first = W.C.A. | last = van Dorst | coauthors = Buck, H.M., Dormans, G.J.M. | publisher = Eindhoven University of Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Organic Chemistry dept | date = 28 Januari 1987 | language = Dutch | pages = 35 pages}}</ref> One third of these events cause no net change, while the remaining two thirds induce a rotation in the [[pi bond]] found between the eleventh and twelfth carbon atoms. In other words, the 11-cis retinal is transformed into the all-trans retinal (''fig B'') in a straightened configuration.<ref>{{cite book|author=Chang, Raymond |title=Chemistry, 6th Ed.|location=New York | publisher=McGraw Hill|year=1998|isbn=0-07-115221-0|oclc=60178489}}</ref> |
|||
[[Vertebrate]] animals ingest retinal directly from meat, or they produce retinal from [[carotenoid]]s – either from [[alpha-Carotene|α-carotene]] or [[β-Carotene|β-carotene]] – both of which are [[carotene]]s. They also produce it from [[beta-Cryptoxanthin|β-cryptoxanthin]], a type of [[xanthophyll]]. These carotenoids must be obtained from plants or other [[photosynthetic]] organisms. No other carotenoids can be converted by animals to retinal. Some carnivores cannot convert any carotenoids at all. The other main forms of vitamin A – [[retinol]] and a partially active form, [[retinoic acid]] – may both be produced from retinal. |
|||
It takes only one rhodopsin isomerization to reliably generate a rod electrical signal.<ref>D. A. Baylor, T. D. Lamb, and K.-W. Yau. ''Responses of retinal rods to single photons.'' J Physiol, 288:613–634, March 1979.</ref><ref>S. Hecht, S. Shlaer, and M. H. Pirenne. ''Energy, quanta, and vision.'' The Journal of General Physiology, 25(6):819–840, 1942.</ref> In mammals, a single rod photon absorption will lead ganglion cells at the output layer of the retina to fire 2-3 additional [[action potential]]s,<ref>H. B. Barlow, W. R. Levick, and M. Yoon. ''Responses to single quanta of light in retinal ganglion cells of the cat.'' Vision Res, Suppl 3:87–101, 1971.</ref> although it may require additional photon absorptions before this signal is detectable above the ganglion cell baseline noise. |
|||
[[Invertebrate]]s such as [[insect]]s and [[squid]] use hydroxylated forms of retinal in their visual systems, which derive from conversion from other [[xanthophylls]]. |
|||
The all-trans retinal configuration, subsequently, does not fit into the binding site of the opsin molecule in the same manner as the 11-cis configuration; as a result, upon [[isomerization]], the trans isomer causes a conformational change in the protein, which triggers a [[G protein]] signaling pathway' including [[transducin]], that results in the generation of an [[electrical impulse]], which is transmitted through the [[optic nerve]] to the [[brain]] for processing. Trans retinal is eventually removed from opsin, and then recycled back to the 11-cis isomer for subsequent use. Enzymes mediate the isomerization of all-trans back to the 11-cis configuration, and rhodopsin is regenerated by a new formation of a [[Schiff base]] linkage, which actuates the binding of the cis isomer to opsin. This is the basic mechanism of the vision cycle. |
|||
==Vitamin A metabolism== |
|||
All-trans-retinal is also an essential component of type I, or microbial, opsins such as [[bacteriorhodopsin]], [[channelrhodopsin]], and [[halorhodopsin]]. In these molecules, light causes the all-trans-retinal to become 13-cis retinal,<ref name=13CIS>De-liang Chen, Guang-yu Wang, Bing Xu and Kun-sheng Hu. ''All-trans to 13-cis retinal isomerization in light-adapted bacteriorhodopsin at acidic pH.'' Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B:Biology. 2002 Apr; 66(3):188-94. {{doi|10.1016/S1011-1344(02)00245-2}}</ref> which then cycles back to all-trans-retinal in the dark state. |
|||
Living organisms produce retinal by irreversible oxidative cleavage of carotenoids.<ref name="von Lintig">{{cite journal |last1=von Lintig |first1=Johannes |last2=Vogt |first2=Klaus |year=2000 |title=Filling the Gap in Vitamin A Research: Molecular Identification of An Enzyme Cleaving Beta-carotene to Retinal |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=275 |issue=16 |pages=11915–11920 |pmid=10766819 |doi=10.1074/jbc.275.16.11915 |doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
<center> |
|||
{|align="center" class="wikitable" |
|||
For example: |
|||
|<center>[[Image:Cis-retinal-3D-balls.png|300px]]</center>||<center>[[Image:Trans-retinal-3D-sticks.png|300px]]</center> |
|||
{{block indent|[[beta-carotene]] + O<sub>2</sub> → 2 retinal,}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|<center>11-''cis''-retinal</center>||<center>all-''trans''-retinal</center> |
|||
catalyzed by a [[beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase]]<ref>{{cite journal |last=Woggon |first=Wolf-D. |year=2002 |title=Oxidative cleavage of carotenoids catalyzed by enzyme models and beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase |journal=Pure and Applied Chemistry |volume=74 |issue=8 |pages=1397–1408 |doi=10.1351/pac200274081397 |doi-access=free}}</ref> or a beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase.<ref name="Kim09">{{cite journal |last1=Kim |first1=Yeong-Su |last2=Kim |first2=Nam-Hee |last3=Yeom |first3=Soo-Jin |last4=Kim |first4=Seon-Won |last5=Oh |first5=Deok-Kun |year=2009 |title=In Vitro Characterization of a Recombinant Blh Protein from an Uncultured Marine Bacterium as a β-Carotene 15,15′-Dioxygenase |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=284 |issue=23 |pages=15781–93 |pmid=19366683 |doi=10.1074/jbc.M109.002618 |pmc=2708875|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
|} |
|||
</center> |
|||
Just as carotenoids are the precursors of retinal, retinal is the precursor of the other forms of vitamin A. Retinal is interconvertible with [[retinol]], the transport and storage form of vitamin A: |
|||
{{block indent|retinal + [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADPH]] + H<sup>+</sup> {{eqm}} retinol + NADP<sup>+</sup>}} |
|||
{{block indent|retinol + [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide|NAD]]<sup>+</sup> {{eqm}} retinal + NADH + H<sup>+</sup>,}} |
|||
catalyzed by [[retinol dehydrogenase]]s (RDHs)<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Lidén |first1=M |last2=Eriksson |first2=U |year=2006 |title=Understanding Retinol Metabolism: Structure and Function of Retinol Dehydrogenases |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=281 |issue=19 |pages=13001–04 |doi=10.1074/jbc.R500027200 |pmid=16428379 |doi-access=free}}</ref> and [[alcohol dehydrogenase]]s (ADHs).<ref name="Duester">{{cite journal |last1=Duester |first1=G |title=Retinoic Acid Synthesis and Signaling during Early Organogenesis |journal=Cell |volume=134 |issue=6 |pages=921–31 |date=September 2008 |pmid=18805086 |pmc=2632951 |doi=10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.002}}</ref> |
|||
Retinol is called vitamin A [[Alcohol (chemistry)|alcohol]] or, more often, simply vitamin A. Retinal can also be oxidized to [[retinoic acid]]: |
|||
{{block indent|retinal + NAD<sup>+</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O → retinoic acid + NADH + H<sup>+</sup> (catalyzed by RALDH)}} |
|||
{{block indent|retinal + O<sub>2</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O → retinoic acid + H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> (catalyzed by retinal oxidase),}} |
|||
catalyzed by [[retinal dehydrogenase]]s<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Lin |first1=Min |last2=Zhang |first2=Min |last3=Abraham |first3=Michael |last4=Smith |first4=Susan M. |last5=Napoli |first5=Joseph L. |year=2003 |title=Mouse Retinal Dehydrogenase 4 (RALDH4), Molecular Cloning, Cellular Expression, and Activity in 9-cis-Retinoic Acid Biosynthesis in Intact Cells |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=278 |issue=11 |pages=9856–9861 |doi=10.1074/jbc.M211417200 |pmid=12519776 |doi-access=free}}</ref> also known as retinaldehyde dehydrogenases (RALDHs)<ref name="Duester"/> as well as [[retinal oxidase]]s.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?enzyme+1.2.3.11 |title=KEGG ENZYME: 1.2.3.11 retinal oxidase |access-date=2009-03-10}}</ref> |
|||
Retinoic acid, sometimes called vitamin A [[carboxylic acid|acid]], is an important signaling molecule and hormone in vertebrate animals. |
|||
==Vision== |
|||
Retinal is a [[conjugated system#Chromophores|conjugated chromophore]]. In the [[Vertebrate eyes]], retinal begins in an 11-''cis''-retinal configuration, which — upon capturing a [[photon]] of the correct wavelength — straightens out into an all-''trans''-retinal configuration. This configuration change pushes against an opsin protein in the [[retina]], which triggers a chemical signaling cascade, which results in [[perception]] of light or images by the brain. The absorbance spectrum of the chromophore depends on its interactions with the opsin protein to which it is bound, so that different retinal-opsin complexes will absorb photons of different wavelengths (i.e., different colors of light). |
|||
===Opsins=== |
|||
[[File:1415_Retinal_Isomers.jpg|thumb|An opsin protein surrounds a molecule of 11-''cis'' retinal, awaiting the arrival of a photon. Once the retinal molecule captures a photon, its configuration change causes it to push against the surrounding opsin protein which may cause the opsin to send a chemical signal to the brain indicating that light has been detected. Retinal is then converted back to its 11-''cis'' configuration by ATP phosphorylation, and the cycle begins again.]] |
|||
[[File:Rhodopsin-transducin.png|thumb|left|Animal GPCR [[rhodopsin]] (rainbow-colored) embedded in a [[lipid bilayer]] (heads red and tails blue) with [[transducin]] below it. G<sub>t</sub>α is colored red, G<sub>t</sub>β blue, and G<sub>t</sub>γ yellow. There is a bound [[guanosine diphosphate|GDP]] molecule in the G<sub>t</sub>α-subunit and a bound '''retinal''' (black) in the rhodopsin. The [[amino-terminus|N-terminus]] terminus of rhodopsin is red and the [[C-terminus]] blue. Anchoring of transducin to the membrane has been drawn in black.]] |
|||
Retinal is bound to [[opsin]]s, which are [[G protein-coupled receptor]]s (GPCRs).<ref name=Casey1988>{{cite journal |last1=Casey |first1=P J |last2=Gilman |first2=A G |title=G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |date=February 1988 |volume=263 |issue=6 |pages=2577–2580 |doi=10.1016/s0021-9258(18)69103-3 |pmid=2830256|s2cid=38970721 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref name=Attwood1994>{{cite journal |last1=Attwood |first1=T. K. |last2=Findlay |first2=J. B. C. |title=Fingerprinting G-protein-coupled receptors |journal=Protein Engineering, Design and Selection |date=1994 |volume=7 |issue=2 |pages=195–203 |doi=10.1093/protein/7.2.195|pmid=8170923 }}</ref> Opsins, like other GPCRs, have seven transmembrane [[alpha-helix|alpha-helices]] connected by six loops. They are found in the [[photoreceptor cell]]s in the [[retina]] of eye. The opsin in the vertebrate [[rod cell]]s is [[rhodopsin]]. The rods form disks, which contain the rhodopsin molecules in their membranes and which are entirely inside of the cell. The [[N-terminus]] head of the molecule extends into the interior of the disk, and the [[C-terminus]] tail extends into the cytoplasm of the cell. The opsins in the [[cone cell]]s are [[OPN1SW]], [[OPN1MW]], and [[OPN1LW]]. The cones form incomplete disks that are part of the [[plasma membrane]], so that the N-terminus head extends outside of the cell. In opsins, retinal binds covalently to a [[lysine]]<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Bownds |first1=Deric |title=Site of Attachment of Retinal in Rhodopsin |journal=Nature |date=December 1967 |volume=216 |issue=5121 |pages=1178–1181 |doi=10.1038/2161178a0 |pmid=4294735|bibcode=1967Natur.216.1178B |s2cid=1657759 }}</ref> in the seventh transmembrane helix<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hargrave |first1=P. A. |last2=McDowell |first2=J. H. |last3=Curtis |first3=Donna R. |last4=Wang |first4=Janet K. |last5=Juszczak |first5=Elizabeth |last6=Fong |first6=Shao-Ling |last7=Mohana Rao |first7=J. K. |last8=Argos |first8=P. |title=The structure of bovine rhodopsin |journal=Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism |date=1983 |volume=9 |issue=4 |pages=235–244 |doi=10.1007/BF00535659 |pmid=6342691|s2cid=20407577 }}</ref><ref name=Palczewski2000>{{cite journal | vauthors = Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T, Behnke CA, Motoshima H, Fox BA, Le Trong I, Teller DC, Okada T, Stenkamp RE, Yamamoto M, Miyano M | display-authors = 6 | title = Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor | journal = Science | volume = 289 | issue = 5480 | pages = 739–45 | date = August 2000 | pmid = 10926528 | doi = 10.1126/science.289.5480.739 | citeseerx = 10.1.1.1012.2275 | bibcode = 2000Sci...289..739P }}</ref><ref name=Murakami2008>{{cite journal | vauthors = Murakami M, Kouyama T | title = Crystal structure of squid rhodopsin | journal = Nature | volume = 453 | issue = 7193 | pages = 363–7 | date = May 2008 | pmid = 18480818 | doi = 10.1038/nature06925 | bibcode = 2008Natur.453..363M | s2cid = 4339970 }}</ref> through a [[Schiff base]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Collins |first1=F. D. |title=Rhodopsin and Indicator Yellow |journal=Nature |date=March 1953 |volume=171 |issue=4350 |pages=469–471 |doi=10.1038/171469a0 |pmid=13046517|bibcode=1953Natur.171..469C |s2cid=4152360 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Pitt |first1=G. A. J. |last2=Collins |first2=F. D. |last3=Morton |first3=R. A. |last4=Stok |first4=Pauline |title=Studies on rhodopsin. 8. Retinylidenemethylamine, an indicator yellow analogue |journal=Biochemical Journal |date=1 January 1955 |volume=59 |issue=1 |pages=122–128 |doi=10.1042/bj0590122 |pmid=14351151|pmc=1216098 }}</ref> Forming the Schiff base linkage involves removing the oxygen atom from retinal and two hydrogen atoms from the free amino group of lysine, giving H<sub>2</sub>O. Retinylidene is the divalent group formed by removing the oxygen atom from retinal, and so opsins have been called [[retinylidene protein]]s. |
|||
Opsins are prototypical [[G protein-coupled receptor]]s (GPCRs).<ref>{{cite journal |last=Lamb |first=T D |year=1996 |title=Gain and kinetics of activation in the G-protein cascade of phototransduction |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=93 |issue=2 |pages=566–570 |pmid=8570596 |doi=10.1073/pnas.93.2.566 |pmc=40092 |bibcode=1996PNAS...93..566L|doi-access=free }}</ref> Cattle rhodopsin, the opsin of the rod cells, was the first GPCR to have its [[Protein primary structure|amino acid sequence]]<ref name=Ovchinnikov1982>{{cite journal |last1=Ovchinnikov |first1=Yu.A. |title=Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: structure-function relationships |journal=FEBS Letters |date=8 November 1982 |volume=148 |issue=2 |pages=179–191 |doi=10.1016/0014-5793(82)80805-3 |pmid=6759163|s2cid=85819100 |doi-access=free |bibcode=1982FEBSL.148..179O }}</ref> and [[Protein tertiary structure|3D-structure]] (via [[X-ray crystallography]]) determined.<ref name="Palczewski2000" /> [[Cattle]] rhodopsin contains 348 [[amino acid]] residues. Retinal binds as chromophore at Lys<sup>296</sup>.<ref name="Palczewski2000" /><ref name=Ovchinnikov1982 /> This lysine is conserved in almost all opsins, only a few opsins have lost it during [[evolution]].<ref name=Guehmann2022>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gühmann M, Porter ML, Bok MJ | title = The Gluopsins: Opsins without the Retinal Binding Lysine | journal = Cells | volume = 11 | issue = 15 | pages = 2441 | date = August 2022 | pmid = 35954284 | doi = 10.3390/cells11152441 | pmc = 9368030 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Opsins without the retinal binding lysine are not light sensitive.<ref name=Katana2019>{{cite journal |last1=Katana |first1=Radoslaw |last2=Guan |first2=Chonglin |last3=Zanini |first3=Damiano |last4=Larsen |first4=Matthew E. |last5=Giraldo |first5=Diego |last6=Geurten |first6=Bart R.H. |last7=Schmidt |first7=Christoph F. |last8=Britt |first8=Steven G. |last9=Göpfert |first9=Martin C. |title=Chromophore-Independent Roles of Opsin Apoproteins in Drosophila Mechanoreceptors |journal=Current Biology |date=September 2019 |volume=29 |issue=17 |pages=2961–2969.e4 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2019.07.036 |pmid=31447373|s2cid=201420079 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2019CBio...29E2961K }}</ref><ref name=Leung2020>{{cite journal |last1=Leung |first1=Nicole Y. |last2=Thakur |first2=Dhananjay P. |last3=Gurav |first3=Adishthi S. |last4=Kim |first4=Sang Hoon |last5=Di Pizio |first5=Antonella |last6=Niv |first6=Masha Y. |last7=Montell |first7=Craig |title=Functions of Opsins in Drosophila Taste |journal=Current Biology |date=April 2020 |volume=30 |issue=8 |pages=1367–1379.e6 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.068 |pmid=32243853|pmc=7252503 |bibcode=2020CBio...30E1367L }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kumbalasiri T, Rollag MD, Isoldi MC, Castrucci AM, Provencio I | title = Melanopsin triggers the release of internal calcium stores in response to light | journal = Photochemistry and Photobiology | volume = 83 | issue = 2 | pages = 273–279 | date = March 2007 | pmid = 16961436 | doi = 10.1562/2006-07-11-RA-964 | s2cid = 23060331 }}</ref> Such opsins may have other functions.<ref name=Leung2020 /><ref name=Guehmann2022 /> |
|||
Although mammals use retinal exclusively as the opsin chromophore, other groups of animals additionally use four chromophores closely related to retinal: 3,4-didehydroretinal (vitamin A<sub>2</sub>), (3''R'')-3-hydroxyretinal, (3''S'')-3-hydroxyretinal (both vitamin A<sub>3</sub>), and (4''R'')-4-hydroxyretinal (vitamin A<sub>4</sub>). Many fish and amphibians use 3,4-didehydroretinal, also called [[dehydroretinal]]. With the exception of the [[diptera]]n suborder [[Cyclorrhapha]] (the so-called higher flies), all [[insect]]s examined use the (''R'')-[[enantiomer]] of 3-hydroxyretinal. The (''R'')-enantiomer is to be expected if 3-hydroxyretinal is produced directly from [[xanthophyll]] carotenoids. Cyclorrhaphans, including ''[[Drosophila]]'', use (3''S'')-3-hydroxyretinal.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Seki |first1=Takaharu |last2=Isono |first2=Kunio |last3=Ito |first3=Masayoshi |last4=Katsuta |first4=Yuko |year=1994 |title=Flies in the Group Cyclorrhapha Use (3S)-3-Hydroxyretinal as a Unique Visual Pigment Chromophore |journal=European Journal of Biochemistry |volume=226 |issue=2 |pages=691–696 |doi=10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb20097.x |pmid=8001586 |doi-access=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Seki |first1=Takaharu |last2=Isono |first2=Kunio |last3=Ozaki |first3=Kaoru |last4=Tsukahara |first4=Yasuo |last5=Shibata-Katsuta |first5=Yuko |last6=Ito |first6=Masayoshi |last7=Irie |first7=Toshiaki |last8=Katagiri |first8=Masanao |year=1998 |title=The metabolic pathway of visual pigment chromophore formation in Drosophila melanogaster: All-trans (3S)-3-hydroxyretinal is formed from all-trans retinal via (3R)-3-hydroxyretinal in the dark |journal=European Journal of Biochemistry |volume=257 |issue=2 |pages=522–527 |doi=10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2570522.x |pmid=9826202 |doi-access=free}}</ref> [[Firefly squid]] have been found to use (4''R'')-4-hydroxyretinal. |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
===Visual cycle=== |
|||
{{main|Visual cycle}} |
|||
[[File:Visual cycle.svg|thumb|right|350x350px|Visual cycle]] |
|||
The visual cycle is a circular [[enzymatic pathway]], which is the front-end of phototransduction. It regenerates 11-''cis''-retinal. For example, the visual cycle of mammalian rod cells is as follows: |
|||
#[[all-trans-retinyl ester|all-''trans''-retinyl ester]] + H<sub>2</sub>O → 11-''cis''-retinol + [[fatty acid]]; [[RPE65]] isomerohydrolases;<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Moiseyev |first1=Gennadiy |last2=Chen |first2=Ying |last3=Takahashi |first3=Yusuke |last4=Wu |first4=Bill X. |last5=Ma |first5=Jian-xing |year=2005 |title=RPE65 is the isomerohydrolase in the retinoid visual cycle |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=102 |issue=35 |pages=12413–12418 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0503460102 |pmid=16116091 |pmc=1194921 |bibcode=2005PNAS..10212413M|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
#[[11-cis-retinol|11-''cis''-retinol]] + NAD<sup>+</sup> → 11-''cis''-retinal + NADH + H<sup>+</sup>; 11-''cis''-retinol dehydrogenases; |
|||
#[[11-cis retinal|11-''cis''-retinal]] + [[aporhodopsin]] → [[rhodopsin]] + H<sub>2</sub>O; forms [[Schiff base]] linkage to [[lysine]], -CH=N<sup>+</sup>H-; |
|||
#rhodopsin + [[photon|hν]] → [[metarhodopsin]] II (i.e., 11-''cis'' [[photoisomerization|photoisomerizes]] to all-''trans''): |
|||
#:(rhodopsin + hν → photorhodopsin → bathorhodopsin → lumirhodopsin → metarhodopsin I → metarhodopsin II); |
|||
#[[metarhodopsin]] II + H<sub>2</sub>O → aporhodopsin + all-''trans''-retinal; |
|||
#[[all-trans-retinal|all-''trans''-retinal]] + NADPH + H<sup>+</sup> → all-''trans''-retinol + NADP<sup>+</sup>; all-''trans''-retinol [[dehydrogenase]]s; |
|||
#all-''trans''-retinol + fatty acid → all-''trans''-retinyl ester + H<sub>2</sub>O; [[lecithin retinol acyltransferase]]s (LRATs).<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Jin |first1=Minghao |last2=Yuan |first2=Quan |last3=Li |first3=Songhua |last4=Travis |first4=Gabriel H. |year=2007 |title=Role of LRAT on the Retinoid Isomerase Activity and Membrane Association of Rpe65 |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=282 |issue=29 |pages=20915–20924 |doi=10.1074/jbc.M701432200 |pmid=17504753 |pmc=2747659|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
Steps 3, 4, 5, and 6 occur in [[rod cell|rod cell outer segments]]; Steps 1, 2, and 7 occur in [[retinal pigment epithelium]] (RPE) cells. |
|||
RPE65 isomerohydrolases are [[homology (biology)|homologous]] with beta-carotene monooxygenases;<ref name="von Lintig"/> the homologous ninaB enzyme in ''Drosophila'' has both retinal-forming carotenoid-oxygenase activity and all-''trans'' to 11-''cis'' isomerase activity.<ref name="Oberhauser08">{{cite journal |last1=Oberhauser |first1=Vitus |last2=Voolstra |first2=Olaf |last3=Bangert |first3=Annette |last4=von Lintig |first4=Johannes |last5=Vogt |first5=Klaus |year=2008 |title=NinaB combines carotenoid oxygenase and retinoid isomerase activity in a single polypeptide |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=105 |issue=48 |pages=19000–5 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0807805105 |pmid=19020100 |pmc=2596218 |bibcode=2008PNAS..10519000O|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
==Microbial rhodopsins== |
|||
{{Main article|Microbial rhodopsin}} |
|||
All-''trans''-retinal is also an essential component of [[microbial]] opsins such as [[bacteriorhodopsin]], [[channelrhodopsin]], and [[halorhodopsin]], which are important in [[bacteria]]l and [[archaea]]l [[anoxygenic photosynthesis]]. In these molecules, light causes the all-''trans''-retinal to become 13-''cis'' retinal, which then cycles back to all-''trans''-retinal in the dark state. These proteins are not evolutionarily related to animal opsins and are not GPCRs; the fact that they both use retinal is a result of [[convergent evolution]].<ref name=13CIS>{{cite journal |doi=10.1016/S1011-1344(02)00245-2 |pmid=11960728 |title=All-trans to 13-cis retinal isomerization in light-adapted bacteriorhodopsin at acidic pH |year=2002 |last1=Chen |first1=De-Liang |last2=Wang |first2=Guang-yu |last3=Xu |first3=Bing |last4=Hu |first4=Kun-Sheng |journal=Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology |volume=66 |issue=3 |pages=188–194|bibcode=2002JPPB...66..188C }}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
American biochemist [[George Wald]] and For his work, Wald won a share of the 1967 [[Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine]] with [[Haldan Keffer Hartline]] and [[Ragnar Granit]].<ref>[://nobelprize.org//medicine/1967/ Nobel Prize in Medicine]</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[ |
*[[ ]] |
||
*[[Sensory nervous system]] |
|||
*[[Visual perception|Vision]] |
|||
*[[Visual |
*[[Visual ]] |
||
*[[Visual phototransduction]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{}} |
||
==Further reading== |
|||
{{Refbegin}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last=Fernald |first=Russell D. |year=2006 |title=Casting a Genetic Light on the Evolution of Eyes |journal=Science |volume=313 |issue=5795 |pages=1914–1918 |doi=10.1126/science.1127889 |pmid=17008522 |bibcode=2006Sci...313.1914F |s2cid=84439732}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Amora |first1=Tabitha L. |last2=Ramos |first2=Lavoisier S. |last3=Galan |first3=Jhenny F. |last4=Birge |first4=Robert R. |year=2008 |title=Spectral Tuning of Deep Red Cone Pigments |journal=Biochemistry |volume=47 |issue=16 |pages=4614–20 |pmid=18370404 |doi=10.1021/bi702069d |pmc=2492582}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Barlow |first1=H.B. |last2=Levick |first2=W.R. |last3=Yoon |first3=M. |year=1971 |title=Responses to single quanta of light in retinal ganglion cells of the cat |journal=Vision Research |volume=11 |issue=Supplement 3 |pages=87–101 |doi=10.1016/0042-6989(71)90033-2 |pmid=5293890}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Baylor |first1=D A |last2=Lamb |first2=T D |last3=Yau |first3=K W |year=1979 |title=Responses of retinal rods to single photons |journal=Journal of Physiology |volume=288 |pages=613–634 |pmid=112243 |doi=10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012716 |pmc=1281447 }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Fan |first1=Jie |last2=Woodruff |first2=Michael L |last3=Cilluffo |first3=Marianne C |last4=Crouch |first4=Rosalie K |last5=Fain |first5=Gordon L |year=2005 |title=Opsin activation of transduction in the rods of dark-reared Rpe65 knockout mice |journal=Journal of Physiology |volume=568 |issue=1 |pages=83–95 |doi=10.1113/jphysiol.2005.091942 |pmid=15994181 |pmc=1474752}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Hecht |first1=Selig |last2=Shlaer |first2=Simon |last3=Pirenne |first3=Maurice Henri |year=1942 |journal=Journal of General Physiology |volume=25 |issue=6 |pages=819–840 |doi=10.1085/jgp.25.6.819 |pmid=19873316 |pmc=2142545 |title=Energy, Quanta, and Vision}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Kawaguchi |first1=Riki |last2=Yu |first2=Jiamei |last3=Honda |first3=Jane |last4=Hu |first4=Jane |last5=Whitelegge |first5=Julian |last6=Ping |first6=Peipei |last7=Wiita |first7=Patrick |last8=Bok |first8=Dean |last9=Sun |first9=Hui |year=2007 |title=A Membrane Receptor for Retinol Binding Protein Mediates Cellular Uptake of Vitamin A |journal=Science |volume=315 |issue=5813 |pages=820–825 |doi=10.1126/science.1136244 |pmid=17255476 |bibcode=2007Sci...315..820K |s2cid=25258551|doi-access=free }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Kloer |first1=Daniel P. |last2=Ruch |first2=Sandra |last3=Al-Babili |first3=Salim |last4=Beyer |first4=Peter |last5=Schulz |first5=Georg E. |year=2005 |title=The Structure of a Retinal-Forming Carotenoid Oxygenase |journal=Science |volume=308 |issue=5719 |pages=267–269 |doi=10.1126/science.1108965 |pmid=15821095 |bibcode=2005Sci...308..267K |s2cid=6318853 }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Luo |first1=Dong-Gen |last2=Xue |first2=Tian |last3=Yau |first3=King-Wai |year=2008 |title=How vision begins: An odyssey |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=105 |issue=29 |pages=9855–9862 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0708405105 |pmid=18632568 |pmc=2481352 |bibcode=2008PNAS..105.9855L|doi-access=free }} Good historical review. |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Prado-Cabrero |first1=Alfonso |last2=Scherzinger |first2=Daniel |last3=Avalos |first3=Javier |last4=Al-Babili |first4=Salim |year=2007 |title=Retinal Biosynthesis in Fungi: Characterization of the Carotenoid Oxygenase CarX from Fusarium fujikuroi |journal=[[Eukaryotic Cell (journal)|Eukaryotic Cell]] |volume=6 |issue=4 |pages=650–657 |doi=10.1128/EC.00392-06 |pmid=17293483 |pmc=1865656}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Racker |first1=Efraim |last2=Stoeckenius |first2=Walther |year=1974 |title=Reconstitution of Purple Membrane Vesicles Catalyzing Light-driven Proton Uptake and Adenosine Triphosphate Formation |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=249 |issue=2 |pages=662–663 |doi=10.1016/S0021-9258(19)43080-9 |pmid=4272126 |doi-access=free}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Sadekar |first1=Sumedha |last2=Raymond |first2=Jason|author3-link=Robert E. Blankenship |last3=Blankenship |first3=Robert E. |year=2006 |title=Conservation of Distantly Related Membrane Proteins: Photosynthetic Reaction Centers Share a Common Structural Core |journal=Molecular Biology and Evolution |volume=23 |issue=11 |pages=2001–2007 |doi=10.1093/molbev/msl079 |pmid=16887904 |doi-access=}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Salom |first1=David |last2=Lodowski |first2=David T. |last3=Stenkamp |first3=Ronald E. |last4=Le Trong |first4=Isolde |last5=Golczak |first5=Marcin |last6=Jastrzebska |first6=Beata |last7=Harris |first7=Tim |last8=Ballesteros |first8=Juan A. |last9=Palczewski |first9=Krzysztof |year=2006 |title=Crystal structure of a photoactivated deprotonated intermediate of rhodopsin |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=103 |issue=44 |pages=16123–16128 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0608022103 |pmid=17060607 |pmc=1637547 |bibcode=2006PNAS..10316123S|doi-access=free }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Schäfer |first1=Günter |last2=Engelhard |first2=Martin |last3=Müller |first3=Volker |year=1999 |title=Bioenergetics of the Archaea |journal=Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews |volume=63 |issue=3 |pages=570–620 |pmid=10477309 |doi=10.1128/MMBR.63.3.570-620.1999 |pmc=103747}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Schmidt |first1=Holger |last2=Kurtzer |first2=Robert |last3=Eisenreich |first3=Wolfgang |last4=Schwab |first4=Wilfried |year=2006 |title=The Carotenase AtCCD1 from Arabidopsis thaliana Is a Dioxygenase |journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry |volume=281 |issue=15 |pages=9845–9851 |doi=10.1074/jbc.M511668200 |pmid=16459333 |doi-access=free}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Send |first1=Robert |last2=Sundholm |first2=Dage |year=2007 |title=Stairway to the conical intersection: A computational study of retinal isomerization |journal=Journal of Physical Chemistry A |volume=111 |issue=36 |pages=8766–8773 |doi=10.1021/jp073908l |pmid=17713894 |bibcode=2007JPCA..111.8766S}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Su |first1=Chih-Ying |last2=Luo |first2=Dong-Gen |last3=Terakita |first3=Akihisa |last4=Shichida |first4=Yoshinori |last5=Liao |first5=Hsi-Wen |last6=Kazmi |first6=Manija A. |last7=Sakmar |first7=Thomas P. |last8=Yau |first8=King-Wai |year=2006 |title=Parietal-Eye Phototransduction Components and Their Potential Evolutionary Implications |journal=Science |volume=311 |issue=5767 |pages=1617–1621 |doi=10.1126/science.1123802 |pmid=16543463 |bibcode=2006Sci...311.1617S |s2cid=28604455 }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Venter |first1=J. Craig |last2=Remington |author-link=Craig Venter |year=2004 |title=Environmental Genome Shotgun Sequencing of the Sargasso Sea |journal=Science |volume=304 |issue=5667 |pages=66–74 |doi=10.1126/science.1093857 |pmid=15001713 |first2=K |last3=Heidelberg |first3=JF |last4=Halpern |first4=AL |last5=Rusch |first5=D |last6=Eisen |first6=JA |last7=Wu |first7=D |last8=Paulsen |first8=I |last9=Nelson |first9=KE |last10=Nelson |first10=W |last11=Fouts |first11=D. E. |last12=Levy |first12=S |last13=Knap |first13=A. H. |last14=Lomas |first14=M. W. |last15=Nealson |first15=K |last16=White |first16=O |last17=Peterson |first17=J |last18=Hoffman |first18=J |last19=Parsons |first19=R |last20=Baden-Tillson |first20=H |last21=Pfannkoch |first21=C |last22=Rogers |first22=Y. H. |last23=Smith |first23=H. O. |bibcode=2004Sci...304...66V |display-authors=8 |citeseerx=10.1.1.124.1840 |s2cid=1454587}} The oceans are full of type 1 rhodopsin. |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Wang |first1=Tao |last2=Jiao |first2=Yuchen |last3=Montell |first3=Craig |year=2007 |title=Dissection of the pathway required for generation of vitamin A and for Drosophila phototransduction |journal=Journal of Cell Biology |volume=177 |issue=2 |pages=305–316 |doi=10.1083/jcb.200610081 |pmid=17452532 |pmc=2064138}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Waschuk |first1=Stephen A. |last2=Bezerra |first2=Arandi G. |last3=Shi |first3=Lichi |last4=Brown |first4=Leonid S. |year=2005 |title=Leptosphaeria rhodopsin: Bacteriorhodopsin-like proton pump from a eukaryote |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=102 |issue=19 |pages=6879–6883 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0409659102 |pmid=15860584 |pmc=1100770 |bibcode=2005PNAS..102.6879W|doi-access=free }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Yokoyama |first1=Shozo |last2=Radlwimmer |first2=F. Bernhard |year=2001 |title=The molecular genetics and evolution of red and green color vision in vertebrates |journal=Genetics |volume=158 |issue=4 |pages=1697–1710 |doi=10.1093/genetics/158.4.1697 |pmid=11545071 |pmc=1461741}} |
|||
*{{cite book |editor-last=Briggs |editor-first=Winslow R. |editor2-last=Spudich |editor2-first=John L. |title=Handbook of Photosensory Receptors |year=2005 |publisher=Wiley |isbn=978-3-527-31019-7}} |
|||
*{{cite web |url=https://www.nobelprize.org/uploads/2018/06/wald-lecture.pdf |title=Nobel Lecture: The Molecular Basis of Visual Excitation |access-date=2009-02-23 |last=Wald |first=George |author-link=George Wald |year=1967}} |
|||
{{Refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
*[http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEC/CC/vision_background.html First Steps of Vision] - National Health Museum |
*[http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEC/CC/vision_background.html First Steps of Vision] - National Health Museum |
||
*[http://www.chemistry.wustl.edu/~edudev/LabTutorials/Vision/Vision.html Vision and Light-Induced Molecular Changes] |
*[http://www.chemistry.wustl.edu/~edudev/LabTutorials/Vision/Vision.html Vision and Light-Induced Molecular Changes] |
||
*[ |
*[://palaeo-electronica.org/2000_1/retinal/vision.htm Retinal Anatomy and Visual Capacities] |
||
*[ |
*[://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/vchemlib/mim/bristol/retinal/retinal_text.htm Retinal] |
||
{{Carotenoids}} |
{{Carotenoids}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:]] |
||
[[Category:Cyclohexenes]] |
|||
[[Category:Photosynthetic pigments]] |
|||
[[Category:Signal transduction]] |
[[Category:Signal transduction]] |
||
[[Category:Vision]] |
|||
[[Category:Vitamin A]] |
|||
[[he:אופסין#רטינל]] |
|||
[[de:Retinal]] |
|||
[[he:רטינל]] |
|||
[[pl:Retinal]] |
|||
[[zh:视黄醛]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 03:35, 29 November 2024

| |
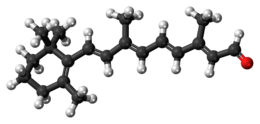
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Retinal
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.760 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H28O | |
| Molar mass | 284.443 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange crystals from petroleum ether[1] |
| Melting point | 61 to 64 °C (142 to 147 °F; 334 to 337 K)[1] |
| Nearly insoluble | |
| Solubility in fat | Soluble |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
retinol; retinoic acid; beta-carotene; dehydroretinal; 3-hydroxyretinal; 4-hydroxyretinal |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use retinal to convert light into metabolic energy. One study suggests that approximately three billion years ago, most living organisms on Earth used retinal, rather than chlorophyll, to convert sunlight into energy. Because retinal absorbs mostly green light and transmits purple light, this gave rise to the Purple Earth hypothesis.[2]
Retinal itself is considered to be a form of vitamin A when eaten by an animal. There are many forms of vitamin A, all of which are converted to retinal, which cannot be made without them. The number of different molecules that can be converted to retinal varies from species to species. Retinal was originally called retinene,[3] and was renamed[4] after it was discovered to be vitamin A aldehyde.[5][6]
Vertebrate animals ingest retinal directly from meat, or they produce retinal from carotenoids – either from α-carotene or β-carotene – both of which are carotenes. They also produce it from β-cryptoxanthin, a type of xanthophyll. These carotenoids must be obtained from plants or other photosynthetic organisms. No other carotenoids can be converted by animals to retinal. Some carnivores cannot convert any carotenoids at all. The other main forms of vitamin A – retinol and a partially active form, retinoic acid – may both be produced from retinal.
Invertebrates such as insects and squid use hydroxylated forms of retinal in their visual systems, which derive from conversion from other xanthophylls.
Vitamin A metabolism
[edit]Living organisms produce retinal by irreversible oxidative cleavage of carotenoids.[7]
For example:
catalyzed by a beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase[8] or a beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase.[9]
Just as carotenoids are the precursors of retinal, retinal is the precursor of the other forms of vitamin A. Retinal is interconvertible with retinol, the transport and storage form of vitamin A:
catalyzed by retinol dehydrogenases (RDHs)[10] and alcohol dehydrogenases (ADHs).[11]
Retinol is called vitamin A alcohol or, more often, simply vitamin A. Retinal can also be oxidized to retinoic acid:
catalyzed by retinal dehydrogenases[12] also known as retinaldehyde dehydrogenases (RALDHs)[11] as well as retinal oxidases.[13]
Retinoic acid, sometimes called vitamin A acid, is an important signaling molecule and hormone in vertebrate animals.
Vision
[edit]Retinal is a conjugated chromophore. In the Vertebrate eyes, retinal begins in an 11-cis-retinal configuration, which — upon capturing a photon of the correct wavelength — straightens out into an all-trans-retinal configuration. This configuration change pushes against an opsin protein in the retina, which triggers a chemical signaling cascade, which results in perception of light or images by the brain. The absorbance spectrum of the chromophore depends on its interactions with the opsin protein to which it is bound, so that different retinal-opsin complexes will absorb photons of different wavelengths (i.e., different colors of light).
Opsins
[edit]

Retinal is bound to opsins, which are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs).[14][15] Opsins, like other GPCRs, have seven transmembrane alpha-helices connected by six loops. They are found in the photoreceptor cells in the retina of eye. The opsin in the vertebrate rod cells is rhodopsin. The rods form disks, which contain the rhodopsin molecules in their membranes and which are entirely inside of the cell. The N-terminus head of the molecule extends into the interior of the disk, and the C-terminus tail extends into the cytoplasm of the cell. The opsins in the cone cells are OPN1SW, OPN1MW, and OPN1LW. The cones form incomplete disks that are part of the plasma membrane, so that the N-terminus head extends outside of the cell. In opsins, retinal binds covalently to a lysine[16] in the seventh transmembrane helix[17][18][19] through a Schiff base.[20][21] Forming the Schiff base linkage involves removing the oxygen atom from retinal and two hydrogen atoms from the free amino group of lysine, giving H2O. Retinylidene is the divalent group formed by removing the oxygen atom from retinal, and so opsins have been called retinylidene proteins.
Opsins are prototypical G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs).[22] Cattle rhodopsin, the opsin of the rod cells, was the first GPCR to have its amino acid sequence[23] and 3D-structure (via X-ray crystallography) determined.[18] Cattle rhodopsin contains 348 amino acid residues. Retinal binds as chromophore at Lys296.[18][23] This lysine is conserved in almost all opsins, only a few opsins have lost it during evolution.[24] Opsins without the retinal binding lysine are not light sensitive.[25][26][27] Such opsins may have other functions.[26][24]
Although mammals use retinal exclusively as the opsin chromophore, other groups of animals additionally use four chromophores closely related to retinal: 3,4-didehydroretinal (vitamin A2), (3R)-3-hydroxyretinal, (3S)-3-hydroxyretinal (both vitamin A3), and (4R)-4-hydroxyretinal (vitamin A4). Many fish and amphibians use 3,4-didehydroretinal, also called dehydroretinal. With the exception of the dipteran suborder Cyclorrhapha (the so-called higher flies), all insects examined use the (R)-enantiomer of 3-hydroxyretinal. The (R)-enantiomer is to be expected if 3-hydroxyretinal is produced directly from xanthophyll carotenoids. Cyclorrhaphans, including Drosophila, use (3S)-3-hydroxyretinal.[28][29] Firefly squid have been found to use (4R)-4-hydroxyretinal.
Visual cycle
[edit]
The visual cycle is a circular enzymatic pathway, which is the front-end of phototransduction. It regenerates 11-cis-retinal. For example, the visual cycle of mammalian rod cells is as follows:
- all-trans-retinyl ester + H2O → 11-cis-retinol + fatty acid; RPE65 isomerohydrolases;[30]
- 11-cis-retinol + NAD+ → 11-cis-retinal + NADH + H+; 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenases;
- 11-cis-retinal + aporhodopsin → rhodopsin + H2O; forms Schiff base linkage to lysine, -CH=N+H-;
- rhodopsin + hν → metarhodopsin II (i.e., 11-cis photoisomerizes to all-trans):
- (rhodopsin + hν → photorhodopsin → bathorhodopsin → lumirhodopsin → metarhodopsin I → metarhodopsin II);
- metarhodopsin II + H2O → aporhodopsin + all-trans-retinal;
- all-trans-retinal + NADPH + H+ → all-trans-retinol + NADP+; all-trans-retinol dehydrogenases;
- all-trans-retinol + fatty acid → all-trans-retinyl ester + H2O; lecithin retinol acyltransferases (LRATs).[31]
Steps 3, 4, 5, and 6 occur in rod cell outer segments; Steps 1, 2, and 7 occur in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells.
RPE65 isomerohydrolases are homologous with beta-carotene monooxygenases;[7] the homologous ninaB enzyme in Drosophila has both retinal-forming carotenoid-oxygenase activity and all-trans to 11-cis isomerase activity.[32]
Microbial rhodopsins
[edit]All-trans-retinal is also an essential component of microbial opsins such as bacteriorhodopsin, channelrhodopsin, and halorhodopsin, which are important in bacterial and archaeal anoxygenic photosynthesis. In these molecules, light causes the all-trans-retinal to become 13-cis retinal, which then cycles back to all-trans-retinal in the dark state. These proteins are not evolutionarily related to animal opsins and are not GPCRs; the fact that they both use retinal is a result of convergent evolution.[33]
History
[edit]The American biochemist George Wald and others had outlined the visual cycle by 1958. For his work, Wald won a share of the 1967 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Haldan Keffer Hartline and Ragnar Granit.[34]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Merck Index, 13th Edition, 8249
- ^ DasSarma, Shiladitya; Schwieterman, Edward W. (2018). "Early evolution of purple retinal pigments on Earth and implications for exoplanet biosignatures". International Journal of Astrobiology. 20 (3) (published 2018-10-11): 241–250. arXiv:1810.05150. doi:10.1017/S1473550418000423. ISSN 1473-5504. S2CID 119341330.
- ^ Wald, George (14 July 1934). "Carotenoids and the Vitamin A Cycle in Vision". Nature. 134 (3376): 65. Bibcode:1934Natur.134...65W. doi:10.1038/134065a0. S2CID 4022911.
- ^ Wald, G. (11 October 1968). "Molecular basis of visual excitation". Science. 162 (3850): 230–9. Bibcode:1968Sci...162..230W. doi:10.1126/science.162.3850.230. PMID 4877437.
- ^ MORTON, R. A.; GOODWIN, T. W. (1 April 1944). "Preparation of Retinene in Vitro". Nature. 153 (3883): 405–406. Bibcode:1944Natur.153..405M. doi:10.1038/153405a0. S2CID 4111460.
- ^ Ball, S.; Goodwin, T. W.; Morton, R. A. (1946). "Retinene1-vitamin A aldehyde". The Biochemical Journal. 40 (5–6): lix. PMID 20341217.
- ^ a b von Lintig, Johannes; Vogt, Klaus (2000). "Filling the Gap in Vitamin A Research: Molecular Identification of An Enzyme Cleaving Beta-carotene to Retinal". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (16): 11915–11920. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.16.11915. PMID 10766819.
- ^ Woggon, Wolf-D. (2002). "Oxidative cleavage of carotenoids catalyzed by enzyme models and beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 74 (8): 1397–1408. doi:10.1351/pac200274081397.
- ^ Kim, Yeong-Su; Kim, Nam-Hee; Yeom, Soo-Jin; Kim, Seon-Won; Oh, Deok-Kun (2009). "In Vitro Characterization of a Recombinant Blh Protein from an Uncultured Marine Bacterium as a β-Carotene 15,15′-Dioxygenase". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (23): 15781–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.002618. PMC 2708875. PMID 19366683.
- ^ Lidén, M; Eriksson, U (2006). "Understanding Retinol Metabolism: Structure and Function of Retinol Dehydrogenases". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (19): 13001–04. doi:10.1074/jbc.R500027200. PMID 16428379.
- ^ a b Duester, G (September 2008). "Retinoic Acid Synthesis and Signaling during Early Organogenesis". Cell. 134 (6): 921–31. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.002. PMC 2632951. PMID 18805086.
- ^ Lin, Min; Zhang, Min; Abraham, Michael; Smith, Susan M.; Napoli, Joseph L. (2003). "Mouse Retinal Dehydrogenase 4 (RALDH4), Molecular Cloning, Cellular Expression, and Activity in 9-cis-Retinoic Acid Biosynthesis in Intact Cells". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (11): 9856–9861. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211417200. PMID 12519776.
- ^ "KEGG ENZYME: 1.2.3.11 retinal oxidase". Retrieved 2009-03-10.
- ^ Casey, P J; Gilman, A G (February 1988). "G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (6): 2577–2580. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(18)69103-3. PMID 2830256. S2CID 38970721.
- ^ Attwood, T. K.; Findlay, J. B. C. (1994). "Fingerprinting G-protein-coupled receptors". Protein Engineering, Design and Selection. 7 (2): 195–203. doi:10.1093/protein/7.2.195. PMID 8170923.
- ^ Bownds, Deric (December 1967). "Site of Attachment of Retinal in Rhodopsin". Nature. 216 (5121): 1178–1181. Bibcode:1967Natur.216.1178B. doi:10.1038/2161178a0. PMID 4294735. S2CID 1657759.
- ^ Hargrave, P. A.; McDowell, J. H.; Curtis, Donna R.; Wang, Janet K.; Juszczak, Elizabeth; Fong, Shao-Ling; Mohana Rao, J. K.; Argos, P. (1983). "The structure of bovine rhodopsin". Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism. 9 (4): 235–244. doi:10.1007/BF00535659. PMID 6342691. S2CID 20407577.
- ^ a b c Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T, Behnke CA, Motoshima H, Fox BA, et al. (August 2000). "Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor". Science. 289 (5480): 739–45. Bibcode:2000Sci...289..739P. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1012.2275. doi:10.1126/science.289.5480.739. PMID 10926528.
- ^ Murakami M, Kouyama T (May 2008). "Crystal structure of squid rhodopsin". Nature. 453 (7193): 363–7. Bibcode:2008Natur.453..363M. doi:10.1038/nature06925. PMID 18480818. S2CID 4339970.
- ^ Collins, F. D. (March 1953). "Rhodopsin and Indicator Yellow". Nature. 171 (4350): 469–471. Bibcode:1953Natur.171..469C. doi:10.1038/171469a0. PMID 13046517. S2CID 4152360.
- ^ Pitt, G. A. J.; Collins, F. D.; Morton, R. A.; Stok, Pauline (1 January 1955). "Studies on rhodopsin. 8. Retinylidenemethylamine, an indicator yellow analogue". Biochemical Journal. 59 (1): 122–128. doi:10.1042/bj0590122. PMC 1216098. PMID 14351151.
- ^ Lamb, T D (1996). "Gain and kinetics of activation in the G-protein cascade of phototransduction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 93 (2): 566–570. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93..566L. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.2.566. PMC 40092. PMID 8570596.
- ^ a b Ovchinnikov, Yu.A. (8 November 1982). "Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: structure-function relationships". FEBS Letters. 148 (2): 179–191. Bibcode:1982FEBSL.148..179O. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(82)80805-3. PMID 6759163. S2CID 85819100.
- ^ a b Gühmann M, Porter ML, Bok MJ (August 2022). "The Gluopsins: Opsins without the Retinal Binding Lysine". Cells. 11 (15): 2441. doi:10.3390/cells11152441. PMC 9368030. PMID 35954284.
- ^ Katana, Radoslaw; Guan, Chonglin; Zanini, Damiano; Larsen, Matthew E.; Giraldo, Diego; Geurten, Bart R.H.; Schmidt, Christoph F.; Britt, Steven G.; Göpfert, Martin C. (September 2019). "Chromophore-Independent Roles of Opsin Apoproteins in Drosophila Mechanoreceptors". Current Biology. 29 (17): 2961–2969.e4. Bibcode:2019CBio...29E2961K. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.07.036. PMID 31447373. S2CID 201420079.
- ^ a b Leung, Nicole Y.; Thakur, Dhananjay P.; Gurav, Adishthi S.; Kim, Sang Hoon; Di Pizio, Antonella; Niv, Masha Y.; Montell, Craig (April 2020). "Functions of Opsins in Drosophila Taste". Current Biology. 30 (8): 1367–1379.e6. Bibcode:2020CBio...30E1367L. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.068. PMC 7252503. PMID 32243853.
- ^ Kumbalasiri T, Rollag MD, Isoldi MC, Castrucci AM, Provencio I (March 2007). "Melanopsin triggers the release of internal calcium stores in response to light". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 83 (2): 273–279. doi:10.1562/2006-07-11-RA-964. PMID 16961436. S2CID 23060331.
- ^ Seki, Takaharu; Isono, Kunio; Ito, Masayoshi; Katsuta, Yuko (1994). "Flies in the Group Cyclorrhapha Use (3S)-3-Hydroxyretinal as a Unique Visual Pigment Chromophore". European Journal of Biochemistry. 226 (2): 691–696. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb20097.x. PMID 8001586.
- ^ Seki, Takaharu; Isono, Kunio; Ozaki, Kaoru; Tsukahara, Yasuo; Shibata-Katsuta, Yuko; Ito, Masayoshi; Irie, Toshiaki; Katagiri, Masanao (1998). "The metabolic pathway of visual pigment chromophore formation in Drosophila melanogaster: All-trans (3S)-3-hydroxyretinal is formed from all-trans retinal via (3R)-3-hydroxyretinal in the dark". European Journal of Biochemistry. 257 (2): 522–527. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2570522.x. PMID 9826202.
- ^ Moiseyev, Gennadiy; Chen, Ying; Takahashi, Yusuke; Wu, Bill X.; Ma, Jian-xing (2005). "RPE65 is the isomerohydrolase in the retinoid visual cycle". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (35): 12413–12418. Bibcode:2005PNAS..10212413M. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503460102. PMC 1194921. PMID 16116091.
- ^ Jin, Minghao; Yuan, Quan; Li, Songhua; Travis, Gabriel H. (2007). "Role of LRAT on the Retinoid Isomerase Activity and Membrane Association of Rpe65". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282 (29): 20915–20924. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701432200. PMC 2747659. PMID 17504753.
- ^ Oberhauser, Vitus; Voolstra, Olaf; Bangert, Annette; von Lintig, Johannes; Vogt, Klaus (2008). "NinaB combines carotenoid oxygenase and retinoid isomerase activity in a single polypeptide". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (48): 19000–5. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10519000O. doi:10.1073/pnas.0807805105. PMC 2596218. PMID 19020100.
- ^ Chen, De-Liang; Wang, Guang-yu; Xu, Bing; Hu, Kun-Sheng (2002). "All-trans to 13-cis retinal isomerization in light-adapted bacteriorhodopsin at acidic pH". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 66 (3): 188–194. Bibcode:2002JPPB...66..188C. doi:10.1016/S1011-1344(02)00245-2. PMID 11960728.
- ^ Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1967
Further reading
[edit]- Fernald, Russell D. (2006). "Casting a Genetic Light on the Evolution of Eyes". Science. 313 (5795): 1914–1918. Bibcode:2006Sci...313.1914F. doi:10.1126/science.1127889. PMID 17008522. S2CID 84439732.
- Amora, Tabitha L.; Ramos, Lavoisier S.; Galan, Jhenny F.; Birge, Robert R. (2008). "Spectral Tuning of Deep Red Cone Pigments". Biochemistry. 47 (16): 4614–20. doi:10.1021/bi702069d. PMC 2492582. PMID 18370404.
- Barlow, H.B.; Levick, W.R.; Yoon, M. (1971). "Responses to single quanta of light in retinal ganglion cells of the cat". Vision Research. 11 (Supplement 3): 87–101. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(71)90033-2. PMID 5293890.
- Baylor, D A; Lamb, T D; Yau, K W (1979). "Responses of retinal rods to single photons". Journal of Physiology. 288: 613–634. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012716. PMC 1281447. PMID 112243.
- Fan, Jie; Woodruff, Michael L; Cilluffo, Marianne C; Crouch, Rosalie K; Fain, Gordon L (2005). "Opsin activation of transduction in the rods of dark-reared Rpe65 knockout mice". Journal of Physiology. 568 (1): 83–95. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.091942. PMC 1474752. PMID 15994181.
- Hecht, Selig; Shlaer, Simon; Pirenne, Maurice Henri (1942). "Energy, Quanta, and Vision". Journal of General Physiology. 25 (6): 819–840. doi:10.1085/jgp.25.6.819. PMC 2142545. PMID 19873316.
- Kawaguchi, Riki; Yu, Jiamei; Honda, Jane; Hu, Jane; Whitelegge, Julian; Ping, Peipei; Wiita, Patrick; Bok, Dean; Sun, Hui (2007). "A Membrane Receptor for Retinol Binding Protein Mediates Cellular Uptake of Vitamin A". Science. 315 (5813): 820–825. Bibcode:2007Sci...315..820K. doi:10.1126/science.1136244. PMID 17255476. S2CID 25258551.
- Kloer, Daniel P.; Ruch, Sandra; Al-Babili, Salim; Beyer, Peter; Schulz, Georg E. (2005). "The Structure of a Retinal-Forming Carotenoid Oxygenase". Science. 308 (5719): 267–269. Bibcode:2005Sci...308..267K. doi:10.1126/science.1108965. PMID 15821095. S2CID 6318853.
- Luo, Dong-Gen; Xue, Tian; Yau, King-Wai (2008). "How vision begins: An odyssey". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (29): 9855–9862. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.9855L. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708405105. PMC 2481352. PMID 18632568. Good historical review.
- Prado-Cabrero, Alfonso; Scherzinger, Daniel; Avalos, Javier; Al-Babili, Salim (2007). "Retinal Biosynthesis in Fungi: Characterization of the Carotenoid Oxygenase CarX from Fusarium fujikuroi". Eukaryotic Cell. 6 (4): 650–657. doi:10.1128/EC.00392-06. PMC 1865656. PMID 17293483.
- Racker, Efraim; Stoeckenius, Walther (1974). "Reconstitution of Purple Membrane Vesicles Catalyzing Light-driven Proton Uptake and Adenosine Triphosphate Formation". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 249 (2): 662–663. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)43080-9. PMID 4272126.
- Sadekar, Sumedha; Raymond, Jason; Blankenship, Robert E. (2006). "Conservation of Distantly Related Membrane Proteins: Photosynthetic Reaction Centers Share a Common Structural Core". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 23 (11): 2001–2007. doi:10.1093/molbev/msl079. PMID 16887904.
- Salom, David; Lodowski, David T.; Stenkamp, Ronald E.; Le Trong, Isolde; Golczak, Marcin; Jastrzebska, Beata; Harris, Tim; Ballesteros, Juan A.; Palczewski, Krzysztof (2006). "Crystal structure of a photoactivated deprotonated intermediate of rhodopsin". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103 (44): 16123–16128. Bibcode:2006PNAS..10316123S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608022103. PMC 1637547. PMID 17060607.
- Schäfer, Günter; Engelhard, Martin; Müller, Volker (1999). "Bioenergetics of the Archaea". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 63 (3): 570–620. doi:10.1128/MMBR.63.3.570-620.1999. PMC 103747. PMID 10477309.
- Schmidt, Holger; Kurtzer, Robert; Eisenreich, Wolfgang; Schwab, Wilfried (2006). "The Carotenase AtCCD1 from Arabidopsis thaliana Is a Dioxygenase". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (15): 9845–9851. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511668200. PMID 16459333.
- Send, Robert; Sundholm, Dage (2007). "Stairway to the conical intersection: A computational study of retinal isomerization". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 111 (36): 8766–8773. Bibcode:2007JPCA..111.8766S. doi:10.1021/jp073908l. PMID 17713894.
- Su, Chih-Ying; Luo, Dong-Gen; Terakita, Akihisa; Shichida, Yoshinori; Liao, Hsi-Wen; Kazmi, Manija A.; Sakmar, Thomas P.; Yau, King-Wai (2006). "Parietal-Eye Phototransduction Components and Their Potential Evolutionary Implications". Science. 311 (5767): 1617–1621. Bibcode:2006Sci...311.1617S. doi:10.1126/science.1123802. PMID 16543463. S2CID 28604455.
- Venter, J. Craig; Remington, K; Heidelberg, JF; Halpern, AL; Rusch, D; Eisen, JA; Wu, D; Paulsen, I; et al. (2004). "Environmental Genome Shotgun Sequencing of the Sargasso Sea". Science. 304 (5667): 66–74. Bibcode:2004Sci...304...66V. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.124.1840. doi:10.1126/science.1093857. PMID 15001713. S2CID 1454587. The oceans are full of type 1 rhodopsin.
- Wang, Tao; Jiao, Yuchen; Montell, Craig (2007). "Dissection of the pathway required for generation of vitamin A and for Drosophila phototransduction". Journal of Cell Biology. 177 (2): 305–316. doi:10.1083/jcb.200610081. PMC 2064138. PMID 17452532.
- Waschuk, Stephen A.; Bezerra, Arandi G.; Shi, Lichi; Brown, Leonid S. (2005). "Leptosphaeria rhodopsin: Bacteriorhodopsin-like proton pump from a eukaryote". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (19): 6879–6883. Bibcode:2005PNAS..102.6879W. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409659102. PMC 1100770. PMID 15860584.
- Yokoyama, Shozo; Radlwimmer, F. Bernhard (2001). "The molecular genetics and evolution of red and green color vision in vertebrates". Genetics. 158 (4): 1697–1710. doi:10.1093/genetics/158.4.1697. PMC 1461741. PMID 11545071.
- Briggs, Winslow R.; Spudich, John L., eds. (2005). Handbook of Photosensory Receptors. Wiley. ISBN 978-3-527-31019-7.
- Wald, George (1967). "Nobel Lecture: The Molecular Basis of Visual Excitation" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-02-23.
External links
[edit]- First Steps of Vision - National Health Museum
- Vision and Light-Induced Molecular Changes
- Retinal Anatomy and Visual Capacities
- Retinal, Imperial College v-chemlib
