Flag of Rwanda: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Altered url. URLs might have been anonymized. Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | #UCB_toolbar |
Adding detail. |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
The [[national flag]] of [[Rwanda]] is a horizontal [[Tricolour (flag)|tricolour]] of light blue, yellow, and green, in a 2:1:1 ratio, charged with a golden sun in the upper [[Fly (flag)|fly-side]] corner. It was adopted on 25 October 2001 and replaced the flag adopted shortly before independence. The design of the flag is defined in the [[Constitution of Rwanda|Rwandan constitution]] and regulations regarding the use and manufacture of the flag are outlined in the country's national flag law (Law no. 34/2008, and subsequent amendments). |
The [[national flag]] of [[Rwanda]] is a horizontal [[Tricolour (flag)|tricolour]] of light blue, yellow, and green, in a 2:1:1 ratio, charged with a golden sun in the upper [[Fly (flag)|fly-side]] corner. It was adopted on 25 October 2001 and replaced the flag adopted shortly before independence. The design of the flag is defined in the [[Constitution of Rwanda|Rwandan constitution]] and regulations regarding the use and manufacture of the flag are outlined in the country's national flag law (Law no. 34/2008, and subsequent amendments). |
||
Rwanda adopted a vertical tricolour of red, yellow, and green following the coup of Gitarama on 28 January 1961, which saw the abolition of the [[Tutsi]]-dominated monarchy and the establishment of a [[Hutu]]-dominated republic. A black "R" was added to the flag's centre in September 1961 |
Rwanda adopted a vertical tricolour of red, yellow, and green following the coup of Gitarama on 28 January 1961, which saw the abolition of the [[Tutsi]]-dominated monarchy and the establishment of a [[Hutu]]-dominated republic. A black "R" was added to the flag's centre in September 1961. The government of the Tutsi-led [[Rwandan Patriotic Front]] (RPF), which overthrew the Hutu-led government and ended the [[Rwandan genocide]] in to change the national flag, arguing that the existing flag had become associated with the genocide. Critics viewed the move as an attempt by the RPF to symbolically assert its rule. |
||
{{TOC limit|3}} |
{{TOC limit|3}} |
||
== Design and symbolism == |
== Design and symbolism == |
||
Rwandan artist and engineer Alphonse Kirimobenecyo designed the flag, which depicts the sun illuminating [[Wildlife of Rwanda|Rwanda's lush vegetation]].{{sfn|Briggs|2023|p=95}}{{sfn|Streissguth|2007|p=69}}{{sfn|Smith|2002}}{{sfn|Vesperini|2001}} As a symbol, the sun represents national unity and transparency, and the enlightenment of the [[Banyarwanda|Rwandan people]].{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=30|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter III, Article 5}} |
Rwandan artist and engineer Alphonse Kirimobenecyo designed the flag, which depicts the sun illuminating [[Wildlife of Rwanda|Rwanda's lush vegetation]].{{sfn|Briggs|2023|p=95}}{{sfn|Streissguth|2007|p=69}}{{sfn|Smith|2002}}{{sfn|Vesperini|2001}} As a symbol, the sun represents national unity and transparency, and the enlightenment of the [[Banyarwanda|Rwandan people]].{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=30|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter III, Article 5}} |
||
The design is described in Chapter II, Article 9 of the [[Constitution of Rwanda]], 2003 (2015 revision). It states: |
The design is described in Chapter II, Article 9 of the [[Constitution of Rwanda]], 2003 (2015 revision). It states: |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==== Dimensions ==== |
==== Dimensions ==== |
||
[[File:Paul Kagame in front of the Rwandan flag, presidential standard, and wooden map.jpg|thumb|Rwandan |
[[File:Paul Kagame in front of the Rwandan flag, presidential standard, and wooden map.jpg|thumb|Rwandan [[Paul Kagame]] sitting beside the Rwandan national flag and [[presidential standard]], 19 May 2022]] |
||
Large flags flown outside government buildings should measure {{convert|130 x 195|cm|abbr=on}} and have no strands; flags flown indoors may have strands. The diameter of the sun should be {{convert|13|cm|abbr=on}} or {{convert|42|cm|abbr=on}} with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be {{convert|13|cm|abbr=on}}, and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be {{convert|14|cm|abbr=on}}. The hoist side should have rings to hoist the flag and a yellow ribbon affixed to it that matches the yellow on the flag.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=26–27|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4}} |
Large flags flown outside government buildings should measure {{convert|130 x 195|cm|abbr=on}} and have no strands; flags flown indoors may have strands. The diameter of the sun should be {{convert|13|cm|abbr=on}} or {{convert|42|cm|abbr=on}} with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be {{convert|13|cm|abbr=on}}, and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be {{convert|14|cm|abbr=on}}. The hoist side should have rings to hoist the flag and a yellow ribbon affixed to it that matches the yellow on the flag.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=26–27|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4}} |
||
Large flags flown at national ceremonies should be presented in the same way as |
Large flags flown at national ceremonies should be presented in the same way as flags flown outside government buildings, but their dimensions differ. Such flags should measure {{convert|150 x 225|cm|abbr=on}}. The diameter of the sun should be {{convert|15|cm|abbr=on}} or {{convert|48.5|cm|abbr=on}} with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be {{convert|15|cm|abbr=on}}, and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be {{convert|16|cm|abbr=on}}.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=28–29|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4}} |
||
Small flags flown inside government offices or on government vehicles should measure {{convert|20 x 30|cm|abbr=on}}. The diameter of the sun should be {{convert|20|mm|abbr=on}} or {{convert|65|mm|abbr=on}} with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be {{convert|20|mm|abbr=on}}, and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be {{convert|22|mm|abbr=on}}.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=27–28|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4}} |
Small flags flown inside government offices or on government vehicles should measure {{convert|20 x 30|cm|abbr=on}}. The diameter of the sun should be {{convert|20|mm|abbr=on}} or {{convert|65|mm|abbr=on}} with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be {{convert|20|mm|abbr=on}}, and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be {{convert|22|mm|abbr=on}}.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=27–28|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4}} |
||
may on a medal, but the flag must not exceed a size of {{convert|140 x 210|mm|abbr=on}}.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=29, 33|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4; and Chapter IV, Article 11}} |
|||
==== Colours ==== |
==== Colours ==== |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
The government of Rwanda has outlined regulations regarding the display and handling of the national flag. Large flags should be flown outside government buildings and during national ceremonies, but lowered once the ceremonies have concluded. They may also be flown by "private buildings and legally recognised associations' buildings" with government approval.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=31–32|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 8}} When raised in front of buildings, the flag raiser should have their back against the front of the building.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=34–35|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 15}} Flags raised in an official capacity should not be lowered unless they are torn, dirty, or old.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=32|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 10}} Small flags should be displayed inside the offices and on the vehicles of top officials such as the president, other officials determined by a presidential order, and Rwandan representatives abroad.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=32|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 9}} |
The government of Rwanda has outlined regulations regarding the display and handling of the national flag. Large flags should be flown outside government buildings and during national ceremonies, but lowered once the ceremonies have concluded. They may also be flown by "private buildings and legally recognised associations' buildings" with government approval.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=31–32|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 8}} When raised in front of buildings, the flag raiser should have their back against the front of the building.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=34–35|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 15}} Flags raised in an official capacity should not be lowered unless they are torn, dirty, or old.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=32|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 10}} Small flags should be displayed inside the offices and on the vehicles of top officials such as the president, other officials determined by a presidential order, and Rwandan representatives abroad.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=32|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 9}} |
||
The national flag |
The national flag held by being sworn into , being legally married. should left hand while their right hand with a stretched palm. who are unable to do so due to disability wear the flag instead.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=33–34|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 13}} The national flag may also be used to cover the coffin of a deceased upon the president's order; nothing may be placed on top of the flag and the flag must not touch the ground.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=34|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 14}} |
||
The national flag takes precedent over other flags of the state. During a parade, it should be flown at the front of the procession.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=35–36|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Articles 16, 17 and 18}} |
The national flag takes precedent over other flags of the state. During a parade, it should be flown at the front of the procession.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=35–36|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Articles 16, 17 and 18}} |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
=== Prohibition of use and desecration === |
=== Prohibition of use and desecration === |
||
, denigrating or damaging the national flag a sentence of 6 to 12 years in prison, a fine of 50,000 to 100,000 [[Rwandan franc]]s, or both.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|p=39|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter VII, Article 30}} A flag that is not the national flag must not be claimed as such; those found guilty of deliberately doing so face a sentence of 1 to 2 years in prison, a fine of 500,000 to 1,000,000 francs, or both.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2018|p=7|loc=Amendment to Law no. 34/2008, Article 30; introduction of Article 31}} Any other deliberate misuse of the flag, such as the use of incorrect colours, is punishable by 1 to 6 months in prison, a fine of 500,000 to 1,000,000 francs, or both.{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2009|pp=38–39, 40|loc=Law no. 34/2008, Chapter VII, Articles 29 and 31}}{{sfn|Government of Rwanda|2018|p=7|loc=Amendment to Law no. 34/2008, Article 30}} |
|||
== History == |
== History == |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
=== 1961–2001 flag === |
=== 1961–2001 flag === |
||
The [[coup of Gitarama]] on 28 January 1961 saw the abolition of the [[Tutsi]]-dominated Kingdom of Rwanda and the establishment of a [[Hutu]]-dominated republic. The coup occurred amid the wider [[Rwandan Revolution]], a period of social change and ethnic violence between the Tutsi minority and Hutu majority.{{sfn|Lemarchand|1970|pp=192–193}} |
The [[coup of Gitarama]] on 28 January 1961 saw the abolition of the [[Tutsi]]-dominated Kingdom of Rwanda and the establishment of a [[Hutu]]-dominated republic. The coup occurred amid the wider [[Rwandan Revolution]], a period of social change and ethnic violence between the Tutsi minority and Hutu majority.{{sfn|Lemarchand|1970|pp=192–193}} [[Grégoire Kayibanda]], proclaimed a new national flag: a vertical tricolour of red, yellow, and green.{{sfn|Taarifa Rwanda|2018}}{{sfn|Nyrop|1969|p=23}} black "R" was added to the centre in late September 1961 to distinguish it.{{sfn|Smith|2002}} The flag was retained upon Rwanda's independence from Belgium on 1 July 1962.{{sfn|Smith|2002}} |
||
The colours of the flag held the following significance: red represented the blood shed for liberation, yellow represented peace and tranquillity, green represented hope and optimism, and black represented gloom and mourning.{{sfn|Smith|2002}}{{sfn|Vesperini|2001}} The "R" stood for Rwanda, revolution, and referendum.{{sfn|Smith|2002}} |
The colours of the flag held the following significance: red represented the blood shed for liberation, yellow represented peace and tranquillity, green represented hope and optimism, and black represented gloom and mourning.{{sfn|Smith|2002}}{{sfn|Vesperini|2001}} The "R" stood for Rwanda, revolution, and referendum.{{sfn|Smith|2002}} |
||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
=== Adoption of the current flag === |
=== Adoption of the current flag === |
||
The national flag was not immediately changed after the Tutsi-led [[Rwandan Patriotic Front]] (RPF) overthrew the Hutu-led government of Rwanda in 1994, which ended the Rwandan genocide.{{sfn|Smith|2002}} |
The national flag was not immediately changed after the Tutsi-led [[Rwandan Patriotic Front]] (RPF) overthrew the Hutu-led government of Rwanda in 1994, which ended the Rwandan genocide.{{sfn|Smith|2002}} new RPF-dominated government announced change the national flag, ostensibly because of the existing flag's association with the Rwandan genocide.{{sfn|Smith|2002}}{{sfn|Vesperini|2001}} A nationwide contest was held to determine the new flag's design, and a submission by Rwandan artist and engineer Alphonse Kirimobenecyo was ultimately selected. The new flag was adopted along with [[Rwanda Nziza|a new anthem]] on 31 December 2001.{{sfn|Briggs|2023|p=95}}{{sfn|Streissguth|2007|p=69}}{{sfn|Smith|2002}}{{sfn|Vesperini|2001}} Rwandans, expressed doubts about the official explanation and viewed the move as an attempt by the RPF to assert its political power.{{sfn|Burnet|2012|p=166}} |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
=== |
=== === |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==== Books ==== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* {{cite book |last=Briggs |first=Philip |title=Rwanda |date=6 December 2023 |publisher=Bradt Travel Guides |isbn=978-1-80469-239-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nNzoEAAAQBAJ |access-date=26 August 2024 |language=en}} |
* {{cite book |last=Briggs |first=Philip |title=Rwanda |date=6 December 2023 |publisher=Bradt Travel Guides |isbn=978-1-80469-239-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nNzoEAAAQBAJ |access-date=26 August 2024 |language=en}} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Burnet |first=Jennie E. |title=Genocide Lives in Us: Women, Memory, and Silence in Rwanda |date=19 November 2012 |publisher=University of Wisconsin Press |location=Madison, WI |isbn=978-0-299-28643-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lASCkgt0E40C |access-date=25 August 2024 |language=en}} |
* {{cite book |last=Burnet |first=Jennie E. |title=Genocide Lives in Us: Women, Memory, and Silence in Rwanda |date=19 November 2012 |publisher=University of Wisconsin Press |location=Madison, WI |isbn=978-0-299-28643-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lASCkgt0E40C |access-date=25 August 2024 |language=en}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * {{cite book |title=Flags and Anthems Manual: London 2012 |date=2012 |publisher=[[London Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games]] |location=London, United Kingdom |page=88 |url=http://doc.rero.ch/record/32076/files/LOC2012_ITR1201_Flags_Manual_Supplement.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150104013349/http://doc.rero.ch/record/32076/files/LOC2012_ITR1201_Flags_Manual_Supplement.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=2015-01-04 |access-date=24 August 2024 |ref={{harvid|LOCOG|2012}}}} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Folarin |first=Sheriff F. |title=Rwanda's Radical Transformation Since the End of the 1994 Genocide against the Tutsi |date=7 August 2023 |publisher=[[Springer Nature]] |isbn=978-3-031-37011-3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_tXPEAAAQBAJ |access-date=27 August 2024 |language=en}} |
* {{cite book |last=Folarin |first=Sheriff F. |title=Rwanda's Radical Transformation Since the End of the 1994 Genocide against the Tutsi |date=7 August 2023 |publisher=[[Springer Nature]] |isbn=978-3-031-37011-3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_tXPEAAAQBAJ |access-date=27 August 2024 |language=en}} |
||
* {{cite book |last1=Kieh |first1=George, Jr. |last2=Agbese |first2=Pita |title=Reconstructing the Authoritarian State in Africa |date=1 October 2013 |publisher=[[Routledge]] |isbn=978-1-135-00759-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wQMiAQAAQBAJ |access-date=27 August 2024 |language=en}} |
* {{cite book |last1=Kieh |first1=George, Jr. |last2=Agbese |first2=Pita |title=Reconstructing the Authoritarian State in Africa |date=1 October 2013 |publisher=[[Routledge]] |isbn=978-1-135-00759-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wQMiAQAAQBAJ |access-date=27 August 2024 |language=en}} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Lemarchand |first=René |title=Rwanda and Burundi |publisher=Praeger Publishers |date=1970 |location=New York |url=https://ufdc.ufl.edu/UF00103151/00001? |oclc=254366212}} |
* {{cite book |last=Lemarchand |first=René |title=Rwanda and Burundi |publisher=Praeger Publishers |date=1970 |location=New York |url=https://ufdc.ufl.edu/UF00103151/00001? |oclc=254366212}} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Nyrop |first=Richard F. |display-authors=etal |title=Area Handbook for Rwanda |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ynMsAAAAYAAJ |year=1969 |publisher=[[U.S. Government Printing Office]] |oclc= 905626482}} |
* {{cite book |last=Nyrop |first=Richard F. |display-authors=etal |title=Area Handbook for Rwanda |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ynMsAAAAYAAJ |year=1969 |publisher=[[U.S. Government Printing Office]] |oclc= 905626482}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |title=Official Gazette no. 16 of 20/04/2009 |url=https://www.rlrc.gov.rw/index.php?eID=dumpFile&t=f&f=74762&token=cb41274d1a4b2d1626672542e40024a521270e26 |location=[[Kigali]] |publisher=[[Government of Rwanda]] |date=20 April 2009 |language=en |ref={{harvid|Government of Rwanda|2009}}}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |title=Official Gazette no. Special of 20/09/2018 |url=https://www.primature.gov.rw/index.php?id=42&no_cache=1&tx_drblob_pi1%5BdownloadUid%5D=579 |url-status=dead |location=[[Kigali]] |publisher=[[Government of Rwanda]] |date=20 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210507044736/https://www.primature.gov.rw/index.php?id=42&no_cache=1&tx_drblob_pi1%5BdownloadUid%5D=579 |archive-date=7 May 2021 |language=en |ref={{harvid|Government of Rwanda|2018}}}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |last=Smith |first=Whitney |author-link=Whitney Smith |display-authors=etal |title=Flag of Rwanda |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/flag-of-Rwanda |website=[[Encyclopædia Britannica]] |publisher=[[Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]] |date=17 May 2002 |orig-date=16 February 2001 |language=en}} |
||
* {{cite book |last=Streissguth |first=Thomas |title=Rwanda in Pictures |date=15 December 2007 |publisher=Twenty-First Century Books |isbn=978-0-8225-8570-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Rfjw_5JL0DsC |access-date=26 August 2024 |language=en}} |
* {{cite book |last=Streissguth |first=Thomas |title=Rwanda in Pictures |date=15 December 2007 |publisher=Twenty-First Century Books |isbn=978-0-8225-8570-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Rfjw_5JL0DsC |access-date=26 August 2024 |language=en}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |title=The Protocol Handbook |url=https://www.minaffet.gov.rw/fileadmin/user_upload/Minaffet/Publications/The_Protocol_Handbook.pdf |publisher=[[Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation (Rwanda)]] |date=2021 |language=en |ref={{harvid|Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation|2021}}}} |
||
{{refend}} |
|||
==== News articles ==== |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
* {{cite news |last=Vesperini |first=Helen |title=Rwanda unveils new flag and anthem |date=31 December 2001 |work=[[BBC News]] |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1735405.stm |access-date=24 August 2024 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20031105035109/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1735405.stm |archive-date=5 November 2003}} |
* {{cite news |last=Vesperini |first=Helen |title=Rwanda unveils new flag and anthem |date=31 December 2001 |work=[[BBC News]] |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1735405.stm |access-date=24 August 2024 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20031105035109/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1735405.stm |archive-date=5 November 2003}} |
||
* {{cite news |title=What Could Have Motivated The 1961 Gitarama Coup In Rwanda? |newspaper=Taarifa Rwanda |date=6 November 2018 |url=https://taarifa.rw/what-could-have-motivated-the-1961-gitarama-coup-in-rwanda/ |access-date=22 September 2021 |archive-date=7 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211007072049/https://taarifa.rw/what-could-have-motivated-the-1961-gitarama-coup-in-rwanda/ |url-status=dead |ref={{harvid|Taarifa Rwanda|2018}}}} |
* {{cite news |title=What Could Have Motivated The 1961 Gitarama Coup In Rwanda? |newspaper=Taarifa Rwanda |date=6 November 2018 |url=https://taarifa.rw/what-could-have-motivated-the-1961-gitarama-coup-in-rwanda/ |access-date=22 September 2021 |archive-date=7 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211007072049/https://taarifa.rw/what-could-have-motivated-the-1961-gitarama-coup-in-rwanda/ |url-status=dead |ref={{harvid|Taarifa Rwanda|2018}}}} |
||
{{refend}} |
|||
==== Government publications ==== |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * {{cite book |title=Flags and Anthems Manual: London 2012 |date=2012 |publisher=[[London Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games]] |location=London, United Kingdom |page=88 |url=http://doc.rero.ch/record/32076/files/LOC2012_ITR1201_Flags_Manual_Supplement.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150104013349/http://doc.rero.ch/record/32076/files/LOC2012_ITR1201_Flags_Manual_Supplement.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=2015-01-04 |access-date=24 August 2024 |ref={{harvid|LOCOG|2012}}}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |title=Official Gazette no. 16 of 20/04/2009 |url=https://www.rlrc.gov.rw/index.php?eID=dumpFile&t=f&f=74762&token=cb41274d1a4b2d1626672542e40024a521270e26 |location=[[Kigali]] |publisher=[[Government of Rwanda]] |date=20 April 2009 |language=en |ref={{harvid|Government of Rwanda|2009}}}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |title=Official Gazette no. Special of 20/09/2018 |url=https://www.primature.gov.rw/index.php?id=42&no_cache=1&tx_drblob_pi1%5BdownloadUid%5D=579 |url-status=dead |location=[[Kigali]] |publisher=[[Government of Rwanda]] |date=20 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210507044736/https://www.primature.gov.rw/index.php?id=42&no_cache=1&tx_drblob_pi1%5BdownloadUid%5D=579 |archive-date=7 May 2021 |language=en |ref={{harvid|Government of Rwanda|2018}}}} |
||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |title=The Protocol Handbook |url=https://www.minaffet.gov.rw/fileadmin/user_upload/Minaffet/Publications/The_Protocol_Handbook.pdf |publisher=[[Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation (Rwanda)]] |date=2021 |language=en |ref={{harvid|Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation|2021}}}} |
||
{{refend}} |
|||
==== Websites ==== |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web |last=Smith |first=Whitney |author-link=Whitney Smith |display-authors=etal |title=Flag of Rwanda |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/flag-of-Rwanda |website=[[Encyclopædia Britannica]] |publisher=[[Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]] |date=17 May 2002 |orig-date=16 February 2001 |language=en}} |
||
{{refend}} |
{{refend}} |
||
Revision as of 02:26, 9 September 2024
 | |
| Use | National flag |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | 31 December 2001 |
| Design | A horizontal tricolour of blue, yellow, and green in a 2:1:1 ratio, charged with a golden sun in the upper fly |
| Designed by | Alphonse Kirimobenecyo |
The national flag of Rwanda is a horizontal tricolour of light blue, yellow, and green, in a 2:1:1 ratio, charged with a golden sun in the upper fly-side corner. It was adopted on 25 October 2001 and replaced the flag adopted shortly before independence. The design of the flag is defined in the Rwandan constitution and regulations regarding the use and manufacture of the flag are outlined in the country's national flag law (Law no. 34/2008, and subsequent amendments).
Rwanda adopted a vertical tricolour of red, yellow, and green following the coup of Gitarama on 28 January 1961, which saw the abolition of the Tutsi-dominated monarchy and the establishment of a Hutu-dominated republic. A black "R" was later added to the flag's centre in September 1961. The government of the Tutsi-led Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF), which in 1994 overthrew the Hutu-led government and ended the Rwandan genocide, announced in 1999 its intention to change the national flag, arguing that the existing flag had become associated with the genocide. Critics viewed the move as an attempt by the RPF to symbolically assert its rule.
Design and symbolism
Rwandan artist and engineer Alphonse Kirimobenecyo designed the flag, which depicts the sun illuminating Rwanda's lush vegetation, as a symbol of unity, patriotism, and hope.[1][2][3][4] As a symbol, the sun represents national unity and transparency, and the enlightenment of the Rwandan people.[5]
The design is described in Chapter II, Article 9 of the Constitution of Rwanda, 2003 (2015 revision). It states:
The national symbols of Rwanda are the national flag, the motto of the Republic, the seal of the Republic and the national anthem. The flag comprises the following colours: from bottom to top a green stripe, followed by a yellow stripe both of which cover half the flag. The upper half is blue and bears on its right-hand side the image of the sun with its rays of golden yellow. The sun and its rays are separated by a blue ring.[6]
Construction
The government of Rwanda has specified sizes, colours, and manufacturing parameters in which the flag is to be made. The flag consists of three horizontal stripes of blue, yellow, and green, from top to bottom.[3] The blue stripe covers half the flag and is twice the height of the yellow and green stripes, which are equal in size.[6][7] The upper fly-side (top right) corner features a golden sun with 24 rays that do not touch the sun's circumference.[6][7][3] The width-to-length ratio of the flag is 2:3.[8][9][a] Rwandan law no. 34/2008 gives specific dimensions for large flags outside or inside government buildings, large flags at national ceremonies, small flags inside government offices or on government vehicles, and flags on medals.[10] Physical flags should be made of 100% polyester and sewn in such a way that the threads connecting the stripes are not visible.[11]
Dimensions

Large flags flown outside government buildings should measure 130 cm × 195 cm (51 in × 77 in) and have no strands; flags flown indoors may have strands. The diameter of the sun should be 13 cm (5.1 in) or 42 cm (17 in) with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be 13 cm (5.1 in), and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be 14 cm (5.5 in). The hoist side should have rings to hoist the flag and a yellow ribbon affixed to it that matches the yellow on the flag.[12]
Large flags flown at national ceremonies should be presented in the same way as the flags flown outside government buildings, but their dimensions differ. Such flags should measure 150 cm × 225 cm (59 in × 89 in). The diameter of the sun should be 15 cm (5.9 in) or 48.5 cm (19.1 in) with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be 15 cm (5.9 in), and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be 16 cm (6.3 in).[13]
Small flags flown inside government offices or on government vehicles should measure 20 cm × 30 cm (7.9 in × 11.8 in). The diameter of the sun should be 20 mm (0.79 in) or 65 mm (2.6 in) with its rays. The space between the tip of the uppermost ray and the top limit of the flag should be 20 mm (0.79 in), and the space between the tip of the rightmost ray and the fly side limit of the flag should be 22 mm (0.87 in).[14]
The flag may be placed on a medal, but the flag must not exceed a size of 140 mm × 210 mm (5.5 in × 8.3 in).[15]
Colours
Rwandan law no. 34/2008 specifies the particular shades of the flag's colours and gives them symbolic significance. Rwandan flags should comply with the following colour codes: blue, Pantene 299 C 2x; green, RAL 6029; yellow, RAL 1023; and golden yellow, RAL 1003.[16] Blue represents happiness and peace, yellow represents economic development, and green represents hope for prosperity.[17]

Protocol
Display and handling

The government of Rwanda has outlined regulations regarding the display and handling of the national flag. Large flags should be flown outside government buildings and during national ceremonies, but lowered once the ceremonies have concluded. They may also be flown by "private buildings and legally recognised associations' buildings" with government approval.[18] When raised in front of buildings, the flag raiser should have their back against the front of the building.[19] Flags raised in an official capacity should not be lowered unless they are torn, dirty, or old.[20] Small flags should be displayed inside the offices and on the vehicles of top officials such as the president, other officials determined by a presidential order, and Rwandan representatives abroad.[21]
The national flag is held by officials when they are being sworn into office, and by couples when they are being legally married. The flag should be held by one's left hand while their right hand is raised with a stretched palm. Those who are unable to do so due to disability wear the flag instead.[22] The national flag may also be used to cover the coffin of a deceased person upon the president's order; nothing may be placed on top of the flag and the flag must not touch the ground.[23]
The national flag takes precedent over other flags of the state. During a parade, it should be flown at the front of the procession.[24]
Half-mast
The national flag must be lowered to half-mast during periods of national mourning and when ordered by the president. The flag may only be lowered after to half-mast after it has first been raised to the end of the flagpole.[25] The flag flies at half-mast during the first week of commemoration of the Rwandan genocide, observed annually from 7 to 13 April, as a sign of national mourning and remembrance.[26] Foreign delegations and organisations in the country are encouraged to do the same to their national flags during this period as a sign of solidarity.[26] When a foreign head of a diplomatic mission dies, the Rwandan national flag is lowered to half-mast at the headquarters of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation and Kigali International Airport.[27]
Prohibition of use and desecration
Disrespecting, denigrating or damaging the national flag carries a sentence of 6 to 12 years in prison, a fine of 50,000 to 100,000 Rwandan francs, or both.[28] A flag that is not the national flag must not be claimed as such; those found guilty of deliberately doing so face a sentence of 1 to 2 years in prison, a fine of 500,000 to 1,000,000 francs, or both.[29] Any other deliberate misuse of the flag, such as the use of incorrect colours, is punishable by 1 to 6 months in prison, a fine of 500,000 to 1,000,000 francs, or both.[30][31]
History
Colonial era
The Kingdom of Rwanda became a part of German East Africa after the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885. This change in relationship between the Germans and Rwandans was symbolised by the former's presentation of the Reichsflagge and a letter of protection to Yuhi V of Rwanda.[32] German East Africa was divided among the Allies following their victory over Germany in World War I. Initial postwar negotiations in 1919 awarded the United Kingdom the entirety of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate, but the Belgians convinced the British to cede to them the kingdoms of Rwanda and Burundi.[32] The Belgian mandate, and later UN trust territory, of Ruanda-Urundi was subsequently established later that year and confirmed by the League of Nations in 1922.[32] The Belgian flag flew in Rwanda from then onwards, until the end of Belgian rule on 1 July 1962.[33]
-
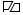 Flag of the German Empire (Reichsflagge)
Flag of the German Empire (Reichsflagge) -
Flag of Belgium (civil)
1961–2001 flag
The coup of Gitarama on 28 January 1961 saw the abolition of the Tutsi-dominated Kingdom of Rwanda and the establishment of a Hutu-dominated republic. The coup occurred amid the wider Rwandan Revolution, a period of social change and ethnic violence between the Tutsi minority and Hutu majority.[34] Grégoire Kayibanda, the Prime Minister of the Provisional Government, proclaimed a new national flag: a vertical tricolour of red, yellow, and green.[35][36] The design was identical to that of the flag of Guinea; a black "R" was added to the centre in late September 1961 to distinguish it.[3] The flag was retained upon Rwanda's independence from Belgium on 1 July 1962.[3]
The colours of the flag held the following significance: red represented the blood shed for liberation, yellow represented peace and tranquillity, green represented hope and optimism, and black represented gloom and mourning.[3][4] The "R" stood for Rwanda, revolution, and referendum.[3]
-
Flag of Guinea
(10 November 1958 – present)
Adoption of the current flag
The national flag was not immediately changed after the Tutsi-led Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) overthrew the Hutu-led government of Rwanda in 1994, which ended the Rwandan genocide.[3] In 1999, the new RPF-dominated government announced it would change the national flag, ostensibly because of the existing flag's association with the Rwandan genocide.[3][4] A nationwide contest was held to determine the new flag's design, and a submission by Rwandan artist and engineer Alphonse Kirimobenecyo was ultimately selected. The new national flag was adopted along with a new national anthem on 31 December 2001.[1][2][3][4] According to American anthropologist Jennie E. Burnet, who interviewed a number of Rwandans before the flag's adoption, critics of the change expressed doubts about the government's official explanation and viewed the move as an attempt by the RPF to assert its political power.[37]
See also
Notes
- ^ Sources published a few years after the flag's adoption, such as Streissguth 2007, p. 69 and Smith 2002, reported a ratio of 1:2.
References
Citations
- ^ a b Briggs 2023, p. 95.
- ^ a b Streissguth 2007, p. 69.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Smith 2002.
- ^ a b c d Vesperini 2001.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 30, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter III, Article 5.
- ^ a b c Constitution of Rwanda 2015, Chapter II, Article 9.
- ^ a b Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 25–26, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 2.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 29, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2020.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 26–29, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 26, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 3.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 26–27, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 28–29, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 27–28, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 29, 33, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter II, Article 4; and Chapter IV, Article 11.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 30–31, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter III, Article 6.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 29–30, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter III, Article 5.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 31–32, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 8.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 34–35, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 15.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 32, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 10.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 32, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 9.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 33–34, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 13.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 34, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 14.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 35–36, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Articles 16, 17 and 18.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 33, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter IV, Article 12.
- ^ a b Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation 2021, p. 30.
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation 2021, p. 9.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, p. 39, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter VII, Article 30.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2018, p. 7, Amendment to Law no. 34/2008, Article 30; introduction of Article 31.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2009, pp. 38–39, 40, Law no. 34/2008, Chapter VII, Articles 29 and 31.
- ^ Government of Rwanda 2018, p. 7, Amendment to Law no. 34/2008, Article 30.
- ^ a b c Kieh & Agbese 2013, p. 162.
- ^ Folarin 2023, p. 185.
- ^ Lemarchand 1970, pp. 192–193.
- ^ Taarifa Rwanda 2018.
- ^ Nyrop 1969, p. 23.
- ^ Burnet 2012, p. 166.
Works cited
- "About the government of Rwanda". Government of Rwanda. 2020. Retrieved 26 August 2024.
- Briggs, Philip (6 December 2023). Rwanda. Bradt Travel Guides. ISBN 978-1-80469-239-4. Retrieved 26 August 2024.
- Burnet, Jennie E. (19 November 2012). Genocide Lives in Us: Women, Memory, and Silence in Rwanda. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-28643-9. Retrieved 25 August 2024.
- "Constitution of the Republic of Rwanda". Kigali: Government of Rwanda. 2015 [2003] – via Constitute Project.
- Flags and Anthems Manual: London 2012 (PDF). London, United Kingdom: London Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 2012. p. 88. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2015. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- Folarin, Sheriff F. (7 August 2023). Rwanda's Radical Transformation Since the End of the 1994 Genocide against the Tutsi. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-031-37011-3. Retrieved 27 August 2024.
- Kieh, George, Jr.; Agbese, Pita (1 October 2013). Reconstructing the Authoritarian State in Africa. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-00759-1. Retrieved 27 August 2024.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Lemarchand, René (1970). Rwanda and Burundi. New York: Praeger Publishers. OCLC 254366212.
- Nyrop, Richard F.; et al. (1969). Area Handbook for Rwanda. U.S. Government Printing Office. OCLC 905626482.
- "Official Gazette no. 16 of 20/04/2009". Kigali: Government of Rwanda. 20 April 2009.
- "Official Gazette no. Special of 20/09/2018". Kigali: Government of Rwanda. 20 September 2018. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021.
- Smith, Whitney; et al. (17 May 2002) [16 February 2001]. "Flag of Rwanda". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- Streissguth, Thomas (15 December 2007). Rwanda in Pictures. Twenty-First Century Books. ISBN 978-0-8225-8570-1. Retrieved 26 August 2024.
- "The Protocol Handbook" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation (Rwanda). 2021.
- Vesperini, Helen (31 December 2001). "Rwanda unveils new flag and anthem". BBC News. Archived from the original on 5 November 2003. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- "What Could Have Motivated The 1961 Gitarama Coup In Rwanda?". Taarifa Rwanda. 6 November 2018. Archived from the original on 7 October 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
External links
 Media related to Flags of Rwanda at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Flags of Rwanda at Wikimedia Commons- Rwanda at Flags of the World





