Aspiviridae
| Ophiovirus | |
|---|---|

| |
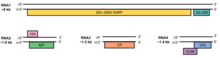
| |
| (top) Electron micrograph of Citrus psorosis ophiovirus; (bottom) Mirafiori lettuce big-vein virus genome | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Negarnaviricota |
| Class: | Milneviricetes |
| Order: | Serpentovirales |
| Family: | Aspiviridae |
| Genus: | Ophiovirus |
| Species | |

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry.[1] It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.[2]
History
[edit]The name Aspiviridae derives from the Latin aspis (snake or viper), referring to the shape, along with the suffix for a virus family -viridae.[3] Ophiovirus derives from the Ancient Greek ophis, "snake", with –virus the suffix for a virus genus.[4] Likewise, Serpentovirales is from "serpent" with -virales the suffix for a virus order.[3] Milneviricetes is in honor of Robert G. Milne, the last author on the first paper describing ophioviruses.[3][5]
Virology
[edit]Structure
[edit]The protein capsid is non-enveloped and has a constant diameter of 1500–2500 nm and a width of 3 nm, or 9 nm. The capsids form kinked circles, which can collapse to form linear duplex structures, much like a spring.[2]
Genome
[edit]Member viruses have segmented, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes. The entire genome is 11000–12000 nucleotides long.[2][6]
Taxonomy
[edit]
The family has one genus, Ophiovirus, which has eight recognized species. Members of both the family and the genus are referred to as ophioviruses.[2] Ophiovirus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species:[7]
- Ophiovirus capsici, Pepper chlorosis associated virus
- Ophiovirus citri, Citrus psorosis virus
- Ophiovirus freesiae, Freesia sneak virus
- Ophiovirus lactucae, Lettuce ring necrosis virus
- Ophiovirus mirafioriense, Mirafiori lettuce big-vein virus
- Ophiovirus ranunculi, Ranunculus white mottle virus
- Ophiovirus tulipae, Tulip mild mottle mosaic virus
- Ophiovirus vaccinii, Blueberry mosaic associated virus
References
[edit]- ^ García, María Laura; Bó, Elena Dal; da Graça, John V.; Gago-Zachert, Selma; Hammond, John; Moreno, Pedro; Natsuaki, Tomohide; Pallás, Vicente; Navarro, Jose A.; Reyes, Carina A.; Luna, Gabriel Robles; Sasaya, Takahide; Tzanetakis, Ioannis E.; Vaira, Anna María; Verbeek, Martin (21 June 2017). "ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Ophioviridae". Journal of General Virology. 98 (6): 1161–1162. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000836. PMC 5656789. PMID 28635587.
- ^ a b c d "ICTV Report Ophioviridae".
- ^ a b c Wolf, Yuri; Krupovic, Mart; Zhang, Yong Zhen; Maes, Piet; Dolja, Valerian; Koonin, Eugene V.; Kuhn, Jens H. "Megataxonomy of negative-sense RNA viruses". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Archived from the original (docx) on January 13, 2019. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ "Aspiviridae – Aspiviridae – Negative-sense RNA Viruses - ICTV". talk.ictvonline.org. Archived from the original on January 15, 2019. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- ^ García, Maria Laura; Dal Bó, Elena; Grau, Oscar; Milne, Robert G. (1 December 1994). "The closely related citrus ringspot and citrus psorosis viruses have particles of novel filamentous morphology". Journal of General Virology. 75 (12): 3585–3590. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-75-12-3585. ISSN 0022-1317. OCLC 107178738. PMID 7996151.
- ^ ICTVdB Management (2006). 00.094.0.01. Ophiovirus. In: ICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database, version 4. Büchen-Osmond, C. (Ed), Columbia University, New York, USA.
- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2024 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Retrieved 13 March 2025.
