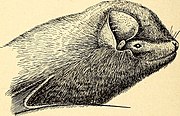
List of miniopterids

Miniopteridae is one of the twenty families of bats in the mammalian order Chiroptera and part of the microbat suborder. A member of this family is called a miniopterid, a bent-winged bat, or long winged bat. They are found in Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia, primarily in caves, forests, shrubland, and grasslands, though some species can also be found in deserts or rocky areas. They range in size from the Shortridge's long-fingered bat, at 3 cm (1 in) plus a 3 cm (1 in) tail, to the great bent-winged bat, at 8 cm (3 in) plus a 7 cm (3 in) tail. Like all bats, miniopterids are capable of true and sustained flight, and have wing lengths ranging from 3 cm (1 in) for many species to 6 cm (2 in) in the western bent-winged bat. They are all insectivorous and eat a variety of insects and spiders.[1] No miniopterids have population estimates, though two species—the Loyalty bent-winged bat and Southeast Asian long-fingered bat—are categorized as endangered species.
The 31 extant species of Miniopteridae are all included in a single genus, Miniopterus. A few extinct prehistoric miniopterid species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.[2]
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (2 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (1 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (2 species) |
| LC | Least concern (19 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (7 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (0 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the miniopterid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted.
Classification
The family Miniopteridae consists of a single genus, Miniopterus, containing 31 species.
Miniopterids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by the reference work Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis, as supported by both the IUCN and the American Society of Mammalogists.[3]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aellen's long-fingered bat
|
M. aelleni Goodman, Maminirina, Friedli-Weyeneth, Bradman, Christidis, Ruedi, & Appleton, 2010 |
Northern Madagascar
|
Size: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest[5] |
LC
|
| African long-fingered bat
|
M. africanus Sanborn, 1936 |
Kenya | Size: Unknown length 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest[6] |
DD
|
| Common bent-wing bat | M. schreibersii (Kuhl, 1817) Twelve subspecies
|
Europe, northern Africa, and western Asia | Size: 5–6 cm (2 in), plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and caves[8] |
VU
|
| Eger's long-fingered bat
|
M. egeri Goodman, Ramasindrazana, Maminirina, Schoeman, & Appleton, 2011 |
Eastern Madagascar
|
Size: 4–6 cm (2 in), plus 4–5 cm (2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest[9] |
LC
|
| Glen's long-fingered bat
|
M. gleni Peterson, Egar, & Mitchell, 1995 |
Madagascar
|
Size: About 7 cm (3 in), plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Caves and forest[10] |
LC
|
| Great bent-winged bat
|
M. tristis (Waterhouse, 1845) Five subspecies
|
Southeastern Asia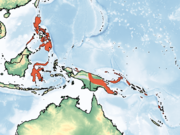
|
Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in), plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail 4–6 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Caves and forest[11] |
LC
|
| Greater long-fingered bat | M. inflatus Thomas, 1903 |
Scattered Sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in), plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[12] |
LC
|
| Griffith's long-fingered bat
|
M. griffithsi Goodman, Maminirina, Bradman, Christidis, & Appleton, 2010 |
Southern Madagascar
|
Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in), plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[13] |
DD
|
| Griveaud's long-fingered bat
|
M. griveaudi Harrison, 1959 |
Northern and western Madagascar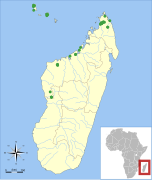
|
Size: 5–6 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Unknown[14] |
DD
|
| Intermediate long-fingered bat
|
M. medius Thomas & Wroughton, 1909 |
Southeastern Asia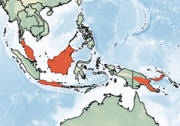
|
Size: 4–6 cm (2 in), plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[15] |
LC
|
| Least long-fingered bat
|
M. minor Peters, 1866 Two subspecies
|
Western and eastern Africa | Size: 5–6 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Unknown[16] |
DD
|
| Lesser long-fingered bat
|
M. fraterculus Thomas & Schwann, 1906 |
Southeastern Africa | Size: 4–6 cm (2 in), plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and caves[17] |
LC
|
| Little bent-wing bat | M. australis Tomes, 1858 Three subspecies
|
Southeastern Asia and eastern Australia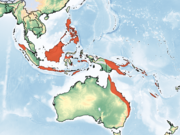
|
Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[18] |
LC
|
| Loyalty bent-winged bat
|
M. robustior Revilliod, 1914 |
New Caledonia | Size: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[19] |
EN
|
| Madagascar long-fingered bat
|
M. brachytragos Goodman, Maminirina, Bradman, Christidis, & Appleton, 2009 |
Northern and western Madagascar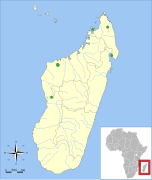
|
Size: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest and rocky areas[20] |
LC
|
| Maghrebian bent-wing bat
|
M. maghrebensis Puechmaille, Allegrini, Benda, Gürün, Srámek, Ibañez, Juste, & Bilgin, 2014 |
Northwestern Africa | Size: About 6 cm (2 in), plus about 6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[21] |
NT
|
| Mahafaly long-fingered bat
|
M. mahafaliensis Goodman, Maminirina, Bradman, Christidis, & Appleton, 2009 |
Southern Madagascar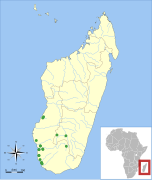
|
Size: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Rocky areas, shrubland, and forest[22] |
LC
|
| Major's long-fingered bat
|
M. majori Thomas, 1906 |
Madagascar
|
Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in), plus 5–6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest and caves[23] |
LC
|
| Manavi long-fingered bat | M. manavi Thomas, 1906 |
Central Madagascar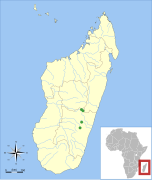
|
Size: About 5 cm (2 in), plus about 4 cm (2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest, rocky areas, and caves[24] |
LC
|
| Montagne d'Ambre long-fingered bat
|
M. ambohitrensis Goodman & Ramasindrazana, 2015 |
Northern Madagascar | Size: 5–6 cm (2 in), plus 4–5 cm (2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest[25] |
LC
|
| Natal long-fingered bat | M. natalensis Smith, 1834 Two subspecies
|
Southern and eastern Africa and Arabian Peninsula | Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in), plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, caves, and desert[26] |
LC
|
| Newton's long-fingered bat
|
M. newtoni Bocage, 1889 |
São Tomé and Príncipe | Size: About 5 cm (2 in), plus about 4 cm (2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest[27] |
DD
|
| Pale bent-wing bat
|
M. pallidus Thomas, 1907 |
Western Asia | Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in), plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Caves and desert[28] |
NT
|
| Peterson's long-fingered bat
|
M. petersoni Goodman, Bradman, Maminirina, Ryan, Christidis, & Appleton, 2008 |
Southeastern Madagascar
|
Size: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Forest[29] |
DD
|
| Philippine long-fingered bat
|
M. paululus Hollister, 1913 |
Southeastern Asia
|
Size: 4–6 cm (2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[30] |
LC
|
| Shortridge's long-fingered bat
|
M. shortridgei Laurie & Hill, 1957 |
Indonesia | Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in), plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail 3–4 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Unknown[31] |
DD
|
| Small bent-winged bat
|
M. pusillus Dobson, 1876 |
Southeastern Asia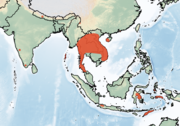
|
Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in), plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[32] |
LC
|
| Small melanesian long-fingered bat | M. macrocneme Revilliod, 1914 |
New Caledonia and New Guinea | Size: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail 3–5 cm (1–2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and caves[33] |
LC
|
| Sororcula long-fingered bat
|
M. sororculus Goodman, Ryan, Maminirina, Fahr, Christidis, & Appleton, 2007 |
Madagascar
|
Size: 5–6 cm (2 in), plus 5–6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[4] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and rocky areas[34] |
LC
|
| Southeast Asian long-fingered bat
|
M. fuscus Bonhote, 1902 |
Japan | Size: 4–6 cm (2 in), plus 5–6 cm (2 in) tail 4–5 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest, inland wetlands, and caves[35] |
EN
|
| Western bent-winged bat
|
M. magnater Sanborn, 1931 Two subspecies
|
Southeastern Asia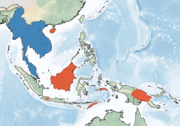
|
Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in), plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail 4–6 cm (2 in) arm/wing length[7] Habitat: Forest and caves[36] |
LC
|
References
- ^ Nowak, p. 221
- ^ "Fossilworks: Miniopterus". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved July 21, 2024.
- ^ Wilson, Reeder, pp. 519–521
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Chernasky; Motis; Burgin, pp. 527–528
- ^ a b Goodman, S. (2017). "Miniopterus aelleni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81629770A95642245. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81629770A95642245.en.
- ^ a b Waldien, D. L.; Webala, P. (2020). "Miniopterus africanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T44859A22073089. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T44859A22073089.en.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Chernasky; Motis; Burgin, pp. 525–526
- ^ a b Cistrone, L.; Russo, D.; Aulagnier, S. (2023). "Miniopterus schreibersii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2023: e.T230918147A230918550. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2023-1.RLTS.T230918147A230918550.en.
- ^ a b Goodman, S. (2017). "Miniopterus egeri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81633146A95642260. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81633146A95642260.en.
- ^ a b Monadjem, A.; Razafimanahaka, J.; Ranivo, J.; Kofoky, A.; Hutson, A. M.; Cardiff, S. G.; Andriafidison, D.; Goodman, S.; Jenkins, R. K. B.; Racey, P. A.; Ratrimomanarivo, F. H. (2017). "Miniopterus gleni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81633094A22046191. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81633094A22046191.en.
- ^ a b Armstrong, K. N.; Wiantoro, S.; Aplin, K. (2021) [amended version of 2019 assessment]. "Miniopterus tristis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T13571A209530159. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T13571A209530159.en.
- ^ a b Monadjem, A.; Schlitter, D. (2017). "Miniopterus inflatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T13565A22104819. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T13565A22104819.en.
- ^ a b Goodman, S. (2017). "Miniopterus griffithsi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81633105A95642250. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81633105A95642250.en.
- ^ a b Juste, J. (2019). "Miniopterus griveaudi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T136752A22035638. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T136752A22035638.en.
- ^ a b Armstrong, K. N.; Wiantoro, S.; Aplin, K. (2021) [amended version of 2019 assessment]. "Miniopterus medius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T13567A209529904. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T13567A209529904.en.
- ^ a b Jacobs, D.; Cotterill, F. P. D.; Taylor, P. J. (2019). "Miniopterus minor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T13568A22105217. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T13568A22105217.en.
- ^ a b Monadjem, A.; Ranivo, J.; Hutson, A. M.; Schlitter, D.; Racey, P. A. (2017). "Miniopterus fraterculus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T13563A22104581. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T13563A22104581.en.
- ^ a b Armstrong, K. N.; Wiantoro, S.; Aplin, K. (2021) [amended version of 2019 assessment]. "Miniopterus australis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T13562A209528942. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T13562A209528942.en.
- ^ a b Waldien, D. L.; Brescia, F. (2020). "Miniopterus robustior". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T13570A22103451. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T13570A22103451.en.
- ^ a b Goodman, S. (2017). "Miniopterus brachytragos". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81629758A95642235. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81629758A95642235.en.
- ^ a b Benda, P.; Piraccini, R. (2017). "Miniopterus maghrebensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81633156A95642265. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T81633156A95642265.en.
- ^ a b Goodman, S. (2017). "Miniopterus mahafaliensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81629764A95642240. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81629764A95642240.en.
- ^ a b Monadjem, A.; Rakotoarivelo, A. R.; Jenkins, R. K. B. (2017). "Miniopterus majori". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T40039A22061249. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T40039A22061249.en.
- ^ a b Goodman, S. (2017). "Miniopterus ambohitrensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T81633128A95642255. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T81633128A95642255.en.
- ^ a b Monadjem, A.; Griffin, M.; Cotterill, F.; Jacobs, D.; Taylor, P. J. (2017). "Miniopterus natalensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T44862A22073129. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T44862A22073129.en.
- ^ a b Juste, J. (2019). "Miniopterus newtoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T136310A22019007. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T136310A22019007.en.
- ^ a b Çoraman, E. (2021). "Miniopterus pallidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T81633088A89457387. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T81633088A89457387.en.
- ^ a b Jenkins, R. K. B.; Rakotoarivelo, A. (2019). "Miniopterus petersoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T81633135A22035230. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T81633135A22035230.en.
- ^ a b Bouillard, N. (2021). "Miniopterus paululus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T136233A22001879. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T136233A22001879.en.
- ^ a b Chiozza, F.; Thong, V. D. (2016). "Miniopterus shortridgei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136827A22044684. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136827A22044684.en.
- ^ a b Bumrungsri, S.; Bates, P. J. J.; Molur, S.; Srinivasulu, C.; Furey, N. (2021). "Miniopterus pusillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T13569A22103542. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T13569A22103542.en.
- ^ a b Armstrong, K. N.; Wiantoro, S.; Aplin, K. (2021) [amended version of 2019 assessment]. "Miniopterus macrocneme". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T136579A209529376. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T136579A209529376.en.
- ^ a b Monadjem, A.; Cardiff, S. G.; Rakotoarivelo, A. R.; Jenkins, R. K. B.; Ratrimomanarivo, F. H. (2017). "Miniopterus sororculus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T136401A22015600. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T136401A22015600.en.
- ^ a b Fukui, D.; Sano, A. (2021) [amended version of 2020 assessment]. "Miniopterus fuscus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T13564A209553784. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T13564A209553784.en.
- ^ a b Armstrong, K. N.; Wiantoro, S.; Aplin, K. (2021) [amended version of 2019 assessment]. "Miniopterus magnater". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T13566A209529644. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T13566A209529644.en.
Sources
- Chernasky, Amy; Motis, Anna; Burgin, Connor, eds. (2023). All the Mammals of the World. Lynx Nature Books. ISBN 978-84-16728-66-4.
- Simmons, Nancy B. (2005). Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
- Nowak, Ronald M. (1994). Walker's Bats of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-4986-2.