Deinodryinus areolatus is an extinct species of Deinodryinus in the wasp family Dryinidae. The species is solely known from an Eocene fossil found in the Baltic region.[1]
| Deinodryinus areolatus Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Dryinidae |
| Genus: | Deinodryinus |
| Species: | †D. areolatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Deinodryinus areolatus (Ponomarenko, 1975)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
History and classification
editDeinodryinus areolatus is known only from a single fossil, the holotype, specimen number PIN No. 964/60, which is housed in the A.A. Borissiak Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, in Moscow. The specimen is composed of a fully complete adult female wasp. The specimen is preserved as an inclusion in a transparent chunk of amber.[1] The amber dates to between forty and forty-five million years old, and, being Baltic amber dispersed in the sea, a more specific type location than the Baltic region is not possible to identify. Deinodryinus areolatus was first studied by the Russian paleoentomologist Nadezdha Ponomarenko in 1975, with a redescription by paleoentomologists Adalgisa Guglielmino and Massimo Olmi, both of the University of Tuscia. Ponomarenko's 1975 type description of the new genus and species was published in the Russian journal Paleontologicheskiy Zhurnal, with the species placed by her into a new genus Electrodryinus.[1] Electrodryinus was subsequently synonymized with Deinodryinus in a 1984 paper by Massimo Olmi, resulting in the current binomial Deinodryinus areolatus. D. areolatus was the first of three Deinodryinus species to be described from the fossil record. Deinodryinus velteni is also known from a fossil preserved in Baltic amber, while Deinodryinus? aptianus is known only from a Mongolian compression fossil in marl.[1]
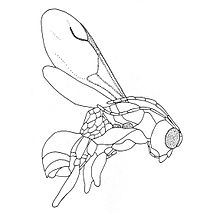
Description
editThe holotype specimen is a complete adult female preserved with areas of the face, vertex, pronotum, scutellum and metanotum obscured. Overall the female is 4.5 millimetres (0.18 in) in length, with antennae that are less than three times the length of the head and macropterous hyaline wings. The antennae are composed of ten segments, densely hairy, and distinctly clavate, (club shaped) in structure. The mandibles have four teeth on each side, which progress from large to small. The tooth size changes in relation to the placement front to back on the mandible. The forewings have three cells at the base that are formed by pigmented veins. The forewings have a pterostigma that is approximately four times as long as it is wide, and a stigmal vein that is not S-shaped. The forelegs have a chelate structure, with the subapical tooth or other teeth.[1]